Milk
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dairy milk is an opaque white liquid produced by the mammary glands of mammals (including monotremes). It provides the primary source of nutrition for newborn mammals before they are able to digest other types of food. The early lactation milk is known as colostrum, and carries the mother's antibodies to the baby. It can reduce the risk of many diseases in the baby. The exact components of raw milk varies by species, but it contains significant amounts of saturated fat, protein and calcium as well as vitamin C. Cow's milk has a pH ranging from 6.4 to 6.8, making it slightly acidic.[1] [2]
Types of consumption
There are two distinct types of milk consumption: a natural source of nutrition for all infant mammals, and a food product for humans of all ages derived from other animals.
Nutrition for infant mammals
In almost all mammals, milk is fed to infants through breastfeeding, either directly or by expressing the milk to be stored and consumed later. Some cultures, historically or currently, continue to use breast milk to feed their children until they are 7 years old.[3]
Food product for humans
In many cultures of the world, especially the Western world, humans continue to consume milk beyond infancy, using the milk of other animals (in particular, cows) as a food product. For millennia, cow milk has been processed into dairy products such as cream, butter, yogurt, kefir, ice cream, and especially the more durable and easily transportable product, cheese. Industrial science has brought us casein, whey protein, lactose, condensed milk, powdered milk, and many other food-additive and industrial products.
Humans are an exception in the natural world for consuming milk past infancy. Most humans[citation needed] lose the ability to fully digest milk after childhood (that is, they become lactose intolerant). The sugar lactose is found only in milk, forsythia flowers, and a few tropical shrubs. The enzyme needed to digest lactose, lactase, reaches its highest levels in the small intestines after birth and then begins a slow decline unless milk is consumed regularly. [4] On the other hand, those groups that do continue to tolerate milk often have exercised great creativity in using the milk of domesticated ungulates, not only of cows, but also sheep, goats, yaks, water buffalo, horses, and camels.
| Country | Litres | Cheese (kg) | Butter (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 183.9 | 19.1 | 5.3 | |
| 145.5 | 18.5 | 1.0 | |
| 129.8 | 10.5 | 2.9 | |
| 122.9 | 20.4 | 3.3 | |
| 116.7 | 16.0 | 4.3 | |
| 119.1 | 9.6 | 1.0 | |
| 112.5 | 22.2 | 5.6 | |
| 111.2 | 12.2 | 3.7 | |
| 106.3 | 11.7 | 3.7 | |
| 94.7 | 12.2 | 3.3 | |
| Source: Introduction to Dairy Science and Technology: Milk History, Consumption, Production, and Composition | |||
Terminology
The term milk is also used for whitish non-animal substitutes such as soy milk, rice milk, almond milk, and coconut milk. Even the regurgitated substance secreted by glands in the mucosa of their upper digestive tract which pigeons feed their young is called crop milk though it bears little resemblance to mammalian milk.
History
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding reliable references (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (September 2008) |

Milking has its advent in the very evolution of placental mammals. While the exact time of its appearance is not known, the immediate ancestors of modern mammals were much like monotremes, including the platypus. Such animals today produce a milk-like substance from glands on the surface of their skin, but without the nipple, for their offspring to drink after hatching from their eggs. Likewise, marsupials, the closest cousin to placental mammals, produce a milk-like substance from a teat-like organ in their pouches. The earliest immediate ancestor of placental mammals known seems to be eomaia, a small creature superficially resembling rodents, that is thought to have lived 125 million years ago, during the Cretaceous era. It almost certainly produced what would be considered milk, in the same way as modern placental mammals.
Animal milk is first known to have been used as human food at the beginning of animal domestication. Cow milk was first used as human food in the Middle East. Goats and sheep were domesticated in the Middle East between 9000 and 8000 BC[citation needed]. Goats and sheep are ruminants: mammals adapted to survive on a diet of dry grass, a food source otherwise useless to humans, and one that is easily stockpiled. The animals were probably first kept for meat and hides[citation needed], but dairying proved to be a more efficient way of turning uncultivated grasslands into sustenance: the food value of an animal killed for meat can be matched by perhaps one year's worth of milk from the same animal, which will keep producing milk — in convenient daily portions — for years.[4]
Around 7000 BC, cattle were being herded in parts of Turkey. There is evidence from DNA extraction of skeletons from the Neolithic period that people in northern Europe were missing the necessary genes to process lactase. Scientists claim it is more likely that the genetic mutation allowing the digestion of milk arose at some point after dairy farming began.[5] The use of cheese and butter spread in Europe, parts of Asia and parts of Africa. Domestic cows, which previously existed throughout much of Eurasia, were then introduced to the colonies of Europe during the Age of exploration.[citation needed]
Milk was first delivered in bottles on January 11, 1878. The day is now remembered as Milk Day and is celebrated annually. The town of Harvard, Illinois also celebrates milk in the summer with a festival known as Milk Days. Theirs is a different tradition meant to celebrate dairy farmers in the "Milk Capital of the World."[6]
Other animal sources
In addition to cows, the following animals provide milk used by humans for dairy products:
In Russia and Sweden, small moose dairies also exist.[7]
Human milk is not produced or distributed industrially or commercially; however, milk banks exist that allow for the collection of donated human milk and its redistribution to infants who may benefit from human milk for various reasons (premature neonates, babies with allergies or metabolic diseases, etc.).
All other female mammals do produce milk, but are rarely or never used to produce dairy products for human consumption.
Modern production
In the Western world today, cow milk is produced on an industrial scale. It is by far the most commonly consumed form of milk in the western world. Commercial dairy farming using automated milking equipment produces the vast majority of milk in developed countries. Types of cattle such as the Holstein have been specially bred for increased milk production. 90% of the dairy cows in the United States and 85% in Great Britain are Holsteins.[4] Other milk cows in the United States include Ayrshire, Brown Swiss, Guernsey, Jersey, and Milking Shorthorn. The largest producers of dairy products and milk today are India followed by the United States[8] and China. In India, Amul, a cooperative owned jointly by 2.6 million small farmers was the engine behind the success of Operation Flood.[citation needed]
This table below shows the numbers of buffalo milk productions. Cow milk is produced in a much wider range.
| Top ten buffalo milk producers — 11 June 2008 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Production (1,000 tonnes) | Footnote | ||
| 56,960 | * | |||
| 21,500 | P | |||
| 2,900 | F | |||
| 2,300 | F | |||
| 930 | F | |||
| 241.5 | F | |||
| 205 | F | |||
| 200 | F | |||
| 35.1 | F | |||
| 31 | F | |||
| 85396902 | A | |||
| No symbol = official figure, P = official figure, F = FAO estimate, * = Unofficial/Semi-official/mirror data, C = Calculated figure A = Aggregate(may include official, semi-official or estimates); |
||||
Price
It was reported in 2007 that with increased worldwide prosperity and the competition of biofuel production for feedstocks, both the demand for and the price of milk had substantially increased world wide. Particularly notable was the rapid increase of consumption of milk in China and the rise of the price of milk in the United States above the government subsidized price.[9]
Physical and chemical structure

Milk is an emulsion or colloid of butterfat globules within a water-based fluid. Each fat globule is surrounded by a membrane consisting of phospholipids and proteins; these emulsifiers keep the individual globules from joining together into noticeable grains of butterfat and also protect the globules from the fat-digesting activity of enzymes found in the fluid portion of the milk. In unhomogenized cow milk, the fat globules average about four micrometers across. The fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K are found within the milkfat portion of the milk.[4]
The largest structures in the fluid portion of the milk are casein protein micelles: aggregates of several thousand protein molecules, bonded with the help of nanometer-scale particles of calcium phosphate. Each micelle is roughly spherical and about a tenth of a micrometer across. There are four different types of casein proteins, and collectively they make up around 80 percent of the protein in milk, by weight. Most of the casein proteins are bound into the micelles. There are several competing theories regarding the precise structure of the micelles, but they share one important feature: the outermost layer consists of strands of one type of protein, kappa-casein, reaching out from the body of the micelle into the surrounding fluid. These Kappa-casein molecules all have a negative electrical charge and therefore repel each other, keeping the micelles separated under normal conditions and in a stable colloidal suspension in the water-based surrounding fluid.[10][4]
Both the fat globules and the smaller casein micelles, which are just large enough to deflect light, contribute to the opaque white color of milk. Skimmed milk, however, appears slightly blue because casein micelles scatter the shorter wavelengths (blue compared to red).
The fat globules contain some yellow-orange carotene, enough in some breeds — Guernsey and Jersey cows, for instance — to impart a golden or "creamy" hue to a glass of milk. The riboflavin in the whey portion of milk has a greenish color, which can sometimes be discerned in skim milk or whey products.[4] Fat-free skim milk has only the casein micelles to scatter light, and they tend to scatter shorter-wavelength blue light more than they do red, giving skim milk a bluish tint.[11]
Milk contains dozens of other types of proteins besides the caseins. They are more water-soluble than the caseins and do not form larger structures. Because these proteins remain suspended in the whey left behind when the caseins coagulate into curds, they are collectively known as whey proteins. Whey proteins make up around twenty percent of the protein in milk, by weight. Lactoglobulin is the most common whey protein by a large margin.[4]
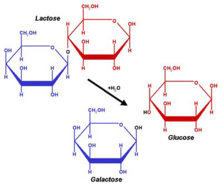
The carbohydrate lactose gives milk its sweet taste and contributes about 40% of whole cow milk's calories. Lactose is a composite of two simple sugars, glucose and galactose. In nature, lactose is found only in milk and a small number of plants.[4] Other components found in raw cow milk are living white blood cells. Mammary-gland cells, various bacteria, and a large number of active enzymes are some other components in milk.[4]
Processing
In most Western countries, a centralised dairy facility processes milk and products obtained from milk (dairy products), such as cream, butter, and cheese. In the United States, these dairies are usually local companies, while in the southern hemisphere facilities may be run by very large nationwide or trans-national corporations (such as Fonterra).
Pasteurization
Pasteurization is used to kill harmful microorganisms by heating the milk for a short time and then cooling it for storage and transportation. Pasteurized milk is still perishable and must be stored cold by both suppliers and consumers. Dairies print expiration dates on each container, after which stores will remove any unsold milk from their shelves. In many countries it is illegal to sell milk that is not pasteurized.[citation needed]
A newer process, Ultra Pasteurization or ultra-high temperature treatment(UHT), heats the milk to a higher temperature for a shorter time. This extends its shelf life and allows the milk to be stored unrefrigerated because of the longer lasting sterilization effect.
Creaming and homogenization
Upon standing for 12 to 24 hours, fresh milk has a tendency to separate into a high-fat cream layer on top of a larger, low-fat milk layer. The cream is often sold as a separate product with its own uses; today the separation of the cream from the milk is usually accomplished rapidly in centrifugal cream separators. The fat globules rise to the top of a container of milk because fat is less dense than water. The smaller the globules, the more other molecular-level forces prevent this from happening. In fact, the cream rises in cow milk much more quickly than a simple model would predict: rather than isolated globules, the fat in the milk tends to form into clusters containing about a million globules, held together by a number of minor whey proteins.[4] These clusters rise faster than individual globules can. The fat globules in milk from goats, sheep, and water buffalo do not form clusters so readily and are smaller to begin with; cream is very slow to separate from these milks.
Milk is often homogenized, a treatment which prevents a cream layer from separating out of the milk. The milk is pumped at high pressures through very narrow tubes, breaking up the fat globules through turbulence and cavitation.[12] A greater number of smaller particles possess more total surface area than a smaller number of larger ones, and the original fat globule membranes cannot completely cover them. Casein micelles are attracted to the newly-exposed fat surfaces; nearly one-third of the micelles in the milk end up participating in this new membrane structure. The casein weighs down the globules and interferes with the clustering that accelerated separation. The exposed fat globules are briefly vulnerable to certain enzymes present in milk, which could break down the fats and produce rancid flavors. To prevent this, the enzymes are inactivated by pasteurizing the milk immediately before or during homogenization.
Homogenized milk tastes blander but feels creamier in the mouth than unhomogenized; it is whiter and more resistant to developing off flavors.[4] Creamline, or cream-top, milk is unhomogenized; it may or may not have been pasteurized. Milk which has undergone high-pressure homogenization, sometimes labeled as "ultra-homogenized," has a longer shelf life than milk which has undergone ordinary homogenization at lower pressures.[13] Homogenized milk may be more digestible than unhomogenized milk.[14]
Concerns exist about the health effects of consuming homogenized milk. Work by Kurt A. Oster, M.D. in the 1960s through the 1980s suggested a link between homogenized milk and arterosclerosis, due to damage to plasmalogen as a result of the release of bovine xanthine oxidase (BXO) from the milk fat globular membrane (MFGM) during homogenization. While Oster's work has been widely criticized, it is apparent that homogenization introduces changes to the MFGM and exposures of its proteins, and the effects of these changes on food safety have not been thoroughly investigated.[14]
Because the fat globules in the milk are reduced in size and encapsulated into liposomes, they pass through the stomach undigested. (The liposomes are protected from the digestive acids.) Because of the tiny size of the fat globules after the milk has been homogenized, the liposomes are then able to pass into the bloodstream through the walls of the intestines, where the damage occurs. The liposomes contain the partially destroyed BXO enzyme. XO is only found in the liver, unless a person drinks homogenized milk. Then it is found in the liposomes that enter the bloodstream, where it begins to attack plasmalogen. (Plasmalogen makes up 30% of the membrane system in human heart muscle cells.) XO can only either use the plasmalogen or destroy it, and in most autopsies of people who have died from heart and circulatory disease - plasmalogen is missing, arterial inner linings are eaten away, and mineral deposits covered in fat and cholesterol create a deadly plaque in the arteries. The addition of synthetic vitamin D in the milk actually enhances the activity of XO. [15]
Nutrition and health
The composition of milk differs widely between species. Factors such as the type of protein; the proportion of protein, fat, and sugar; the levels of various vitamins and minerals; and the size of the butterfat globules and the strength of the curd are among those than can vary.[16] For example:
- Human milk contains, on average, 1.1% protein, 4.2% fat, 7.0% lactose (a sugar), and supplies 72 kcal of energy per 100 grams.
- Cow milk contains, on average, 3.4% protein, 3.6% fat, and 4.6% lactose, 0.7% minerals[17] and supplies 66 kcal of energy per 100 grams. See also Nutritional value further on.
Donkey and horse milk have the lowest fat content, while the milk of seals and whales can contain more than 50% fat.[18][19] High fat content is not unique to aquatic animals, as guinea pig milk has an average fat content of 46%.[20]
Nutritional value
| This article is written like an advertisement. Please help rewrite this article from a neutral point of view. For blatant advertising that would require a fundamental rewrite to become encyclopedic, use {{db-spam}} to mark for speedy deletion. (November 2008) |
| Cow milk (whole) Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy 60 kcal 250 kJ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 100 ml corresponds to 103 g.[21] Percentages are relative to US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient database |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Processed milk began containing differing amounts of fat during the 1950s. A serving (1 cup or 250 ml) of 2%-fat milk contains 285 mg of calcium, which represents 22% to 29% of the daily recommended intake (DRI) of calcium for an adult. Depending on the age, milk contains 8 grams of protein, and a number of other nutrients (either naturally or through fortification)including:
- Biotin
- pantothenic acid
- Iodine
- Potassium
- Magnesium
- Selenium
- Thiamine
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B12
- Riboflavin
- Vitamins D
- Vitamin K
The amount of calcium from milk that is absorbed by the human body is disputed.[22][23] Calcium from dairy products has a greater bioavailability than calcium from certain vegetables, such as spinach, that contain high levels of calcium-chelating agents,[24] but a similar or lesser bioavailability than calcium from low-oxalate vegetables such as kale, broccoli, or other vegetables in the Brassica genus.[25]
Medical research
Studies show possible links between low-fat milk consumption and reduced risk of arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, colorectal cancer and obesity. Overweight individuals who drink milk may benefit from decreased risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.[26] One study has shown that for women desiring to have a child, those who consume full fat dairy products may actually slightly increase their fertility, while those consuming low fat dairy products may slightly reduce their fertility due to interference with ovulation. However, studies in this area are still inconsistent.[27] Milk is a source of Conjugated linoleic acid, a fatty acid that inhibits several types of cancer in mice.[citation needed] CLA has been shown to kill human skin cancer, colorectal cancer and breast cancer cells in vitro studies, and may help lower cholesterol and prevent atherosclerosis; CLA is present only in milk from grass-fed cows.[citation needed]
Controversy
Other studies suggest that milk consumption may increase the risk of suffering from certain health problems. Cow milk allergy (CMA) is as an immunologically mediated adverse reaction to one or more cow milk proteins. Rarely is it severe enough to cause death.[28] Milk contains casein, a substance that breaks down in the human stomach to produce casomorphin, an opioid peptide. In the early 1990s it was hypothesized that casomorphin can cause or aggravate autism,[29][30] and casein-free diets are widely promoted. Studies supporting these claims have had significant flaws, and the data are inadequate to guide autism treatment recommendations.[30] Studies described in the book The China Study note a correlation between casein intake and the promotion of cancer cell growth when exposed to carcinogens. However other studies have shown whey protein offers a protective effect against colon cancer. [31]
A study demonstrated that men who drink a large amount of milk and consume dairy products were at a slightly increased risk of developing Parkinson's disease; the effect for women was smaller.[32] The reason behind this is not fully understood, and it also remains unclear why there is less of a risk for women.[32][33] Several sources suggest a correlation between high calcium intake (2000 mg per day, or twice the US recommended daily allowance, equivalent to six or more glasses of milk per day) and prostate cancer.[34] A large study specifically implicates dairy, i.e., low-fat milk and other dairy to which vitamin A palmitate has been added.[35][36] A review published by the World Cancer Research Fund and the American Institute for Cancer Research states that at least eleven human population studies have linked excessive dairy product consumption and prostate cancer,[37] however randomized clinical trial data with appropriate controls only exists for calcium, not dairy produce, where there was no correlation.[38] Medical studies have also shown a possible link between milk consumption and the exacerbation of diseases such as Crohn’s Disease,[39] Hirschsprung's disease–mimicking symptoms in babies with existing cow milk allergies,[40] severe gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants and children hypersenstitive to milk,[citation needed] and the aggravation of Behçet's disease.[41]
Bovine growth hormone supplementation
Since November 1993, with FDA approval, Monsanto has been selling recombinant bovine somatotropin (rbST), also called rBGH, to dairy farmers. Cows produce bovine growth hormone naturally, but many producers administer additional rBGH because it increase milk production. Bovine growth horome also stimulates liver production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1). If rbST-treated cows produced milk with higher levels of IGF1 this would be of medical concern, because IGF1 stimulates cancer growth in humans. Elevated levels of IGF1 in human blood has been linked to increased rates of breast, colon, and prostate cancer[42][43]. Testing has shown that milk from cows given rBGH does not contain more IGF1 than milk from cows that were not given rBGH.[44]. No study has indicated that consumption of rBST-produced milk increases IGF1 levels in humans, nor has any study demonstrated an increased risk of any disease between those consuming rBST and non-rBST produced milk. However, many groups remain concerned. The EU has recommended against Monsanto milk[45] On June 9, 2006 the largest milk processor in the world and the two largest supermarkets in the United States--Dean Foods, Wal-Mart, and Kroger--announced that they are "on a nationwide search for rBGH-free milk."[46] Milk from cows given rBST may be sold in the United States, and the FDA stated that no significant difference has been shown between milk derived from rBST-treated and that from non-rBST-treated cows.[47] Milk that advertises that it comes from cows not treated with rBST is required to state this finding on its label.
Cows receiving rBGH supplements may more frequently contract an udder infection known as mastitis[48]. Problems with mastitis have led to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and Japan banning milk from rBST treated cows. Mastitis, among other diseases, may be responsible for the fact that levels of white blood cells in milk vary naturally.[49][50] Although not considered a human health issue by most authorities, a minority of scientists believe that these cells could contribute to the transmission of bovine paratubeculosis to humans.[51] The existing empirical evidence is largely inconclusive.
Lactose intolerance
Lactose, the disaccharide sugar component of all milk must be cleaved in the small intestine by the enzyme lactase in order for its constituents (galactose and glucose) to be absorbed. The production of this enzyme declines significantly after weaning in all mammals. Consequently, many humans become unable to properly digest lactose as they mature. There is a great deal of variance, with some individuals reacting badly to even small amounts of lactose, some able to consume moderate quantities, and some able to consume large quantities of milk and other dairy products without problems. When an individual consumes milk without producing sufficient lactase, they may suffer diarrhea, intestinal gas, cramps and bloating, as the undigested lactose travels through the gastrointestinal tract and serves as nourishment for intestinal microflora who excrete gas, a process known as anaerobic respiration.
Lactose intolerance is a natural process and there is no reliable way to prevent or reverse it. Lactase is readily available in pill form, and many individuals can use it to briefly increase their tolerance for dairy products.
Ethical concerns
Vegans and some vegetarians do not consume milk for a variety of reasons. They may object to the treatment of cattle or to separating the mother and calf, veal production, and slaughter of "used" cows.
Nutrition - comparison by animal source
Milk composition analysis, per 100 grams
| Constituents | unit | Cow | Goat | Sheep | Water Buffalo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | g | 87.8 | 88.9 | 83.0 | 81.1 |
| Protein | g | 3.2 | 3.1 | 5.4 | 4.5 |
| Fat | g | 3.9 | 3.5 | 6.0 | 8.0 |
| Carbohydrate | g | 4.8 | 4.4 | 5.1 | 4.9 |
| Energy | kcal | 66 | 60 | 95 | 110 |
| kJ | 275 | 253 | 396 | 463 | |
| Sugars (lactose) | g | 4.8 | 4.4 | 5.1 | 4.9 |
| Fatty acids: | |||||
| Saturated | g | 2.4 | 2.3 | 3.8 | 4.2 |
| Mono-unsaturated | g | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 1.7 |
| Polyunsaturated | g | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Cholesterol | mg | 14 | 10 | 11 | 8 |
| Calcium | IU | 120 | 100 | 170 | 195 |
Source: McCane, Widdowson, Scherz, Kloos.[1]
These compositions vary by breed, animal, and point in the lactation period. Jersey cows produce milk of about 5.2% fat, Zebu cows produce milk of about 4.7% fat, Brown Swiss cows produce milk of about 4.0% fat, and Holstein-Friesian cows produce milk of about 3.6% fat. The protein range for these four breeds is 3.3% to 3.9%, while the lactose range is 4.7% to 4.9%. [52]
Milk fat percentages in all dairy breeds vary according to digestible fiber, starch and oil intakes[citation needed], and can therefore be manipulated by dairy farmers' diet formulation strategies. Mastitis infection can cause fat levels to decline.[53]
Varieties and brands
Milk products are sold in a number of varieties based on types/degrees of
- age (e.g., cheddar),
- additives (e.g., vitamins),
- coagulation (e.g., cottage cheese),
- farming method (e.g., organic, grass-fed).
- fat content (e.g., half and half),
- fermentation (e.g., buttermilk),
- flavoring (e.g., chocolate),
- homogenization (e.g., raw milk),
- mammal (e.g., cow, goat, sheep),
- packaging (e.g., bottle),
- sterilization (e.g., pasteurization),
- water content (e.g., dry milk),
Organic milk (in the United States) or bio-milk & biologique milk (in Europe) is milk produced without the use of chemical herbicides or pesticides, and generally with more natural fertilizers and higher standards for the animals[citation needed], and is now easy to find on the shelves in many areas. Demeter certified milk is produced with biodynamic agriculture methods and is similar in standards to organic milk and biological milk, with a few special farm procedures added that are biodynamic-specific.
Additives and flavoring
In countries where the cattle (and often the people) live indoors, commercially sold milk commonly has vitamin D added to it to make up for lack of exposure to UVB radiation.
Reduced fat milks often have added vitamin A to compensate for the loss of the vitamin during fat removal; in the United States this results in reduced fat milks having a higher vitamin A content than whole milk.[54]
To aid digestion in those with lactose intolerance, milk is available in some areas with added bacterial cultures such as Lactobacillus acidophilus ("acidophilus milk") and bifidobacteria ("a/B milk").[55] Another milk with Lactococcus lactis bacteria cultures ("cultured buttermilk") is often used in cooking to replace the traditional use of naturally soured milk, which has become rare due to the ubiquity of pasteurization which kills the naturally occurring lactococcus bacteria.[56]
Milk often has flavoring added to it for better taste or as a means of improving sales. Chocolate flavored milk has been sold for many years and has been followed more recently by such other flavors as strawberry and banana.
South Australia has the highest consumption of flavored milk per person in the world, where Farmers Union Iced Coffee outsells Coca-Cola, a success shared only by Inca Kola in Peru and Irn-Bru in Scotland.
Distribution
| This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (August 2008) |
Because milk spoils so easily, it should, ideally, be distributed as quickly as possible. In many countries milk used to be delivered to households daily, but economic pressure has made milk delivery much less popular, and in many areas daily delivery is no longer available. People buy it chilled at grocery or convenience stores or similar retail outlets. Prior to the widespread use of plastics, milk was sold in wax-coated paper containers; prior to that milk was often distributed to consumers in glass bottles; and before glass bottles, in bulk that was ladled into the customer's container.
In the UK, milk can be delivered daily by a milkman who travels his local milk round (route) using a milk float (often battery powered) during the early hours. Milk is delivered in 1 pint glass bottles with aluminium foil tops. Silver top denotes full cream unhomogenized; red top full cream homogenized; red/silver top semi-skimmed; blue/silver check top skimmed; and gold top channel island.
Empty bottles are rinsed before being left outside for the milkman to collect and take back to the dairy for washing and reuse. Currently many milkmen operate franchises as opposed to being employed by the dairy and payment is made at regular intervals, by leaving a check; by cash collection; or direct debit.
Although there was a steep decline in doorstep delivery sales throughout the 1990s, the service is still prominent, as dairies have diversified and the service is becoming more popular again. The doorstep delivery of milk is seen as part of the UK's heritage, and is relied upon by people up and down the country.
In Australia and New Zealand, milk is no longer distributed in glass bottles, due to declining sales and the introduction of long life packaging (UHT). Milk is generally sold in plastic 2 and 3 liter bottles and cardboard cartons as well as the long life varieties.
In rural India and Pakistan, milk is delivered daily by a local milkman carrying bulk quantities in a metal container, usually on a bicycle; and in other parts of metropolitan India and Pakistan, milk is usually bought or delivered in a plastic bags or cartons via-shops or supermarkets.
In the United States, glass milk bottles have been mostly replaced with milk cartons (tall paper boxes with a square cross-section and a peaked top that can be folded outward upon opening to form a spout) and plastic jugs. Gallons of milk are almost always sold in jugs, while half-gallons and quarts may be found in both paper cartons and plastic jugs, and smaller sizes are almost always in cartons. Recently, milk has been sold in smaller resealable bottles made to fit in automobile cup holders. These individual serving sizes are also sold in flavored varieties.
The half-pint milk carton is the traditional unit as a component of school lunches. In the U.S., pictures of missing children were printed on the larger milk cartons as a public service until it was determined that this was disturbing to children.
Milk preserved by the UHT process is sold in cartons often called a brick that lack the peak of the traditional milk carton. Milk preserved in this fashion does not need to be refrigerated before opening and has a longer shelf life than milk in ordinary packaging. It is more typically sold unrefrigerated on the shelves in Europe and Latin America than in the United States.
Glass milk containers are now rare. Most people purchase milk in bags, plastic jugs or plastic-coated paper cartons. Ultraviolet (UV) light from fluorescent lighting can alter the flavor of milk, so many companies that once distributed milk in transparent or highly translucent containers are now using thicker materials that block the UV light. Many people feel that such "UV protected" milk tastes better.
Milk comes in a variety of containers with local variants:
- Australia and New Zealand: Distributed in a variety of sizes, most commonly in aseptic cartons for up to 1 litres, and plastic screw-top bottles beyond that with the following volumes; 1.1L, 2L, and 3L. 1 litre Bags are starting to appear in supermarkets, but have not yet proved popular. Most UHT-milk is packed in 1 or 2 litre paper containers with a sealed plastic spout.
- Brazil: Used to be sold in cooled 1 litre bags, just like in South Africa. Nowadays the most common form is 1 litre aseptic cartons containing UHT skimmed, semi-skimmed or whole milk, although the plastic bags are still in use for pasteurized milk. Higher grades of pasteurized milk can be found in cartons or plastic bottles. Sizes other than 1 liter are rare.
- Canada: 1.33 litre plastic bags (sold as 4 litres in 3 bags) are widely available in some areas (especially the Maritimes, Ontario and Quebec), although the 4 litre plastic jug has supplanted them in western Canada. Other common packaging sizes are 2 litre, 1 litre, 500 millilitre, and 250 millilitre cartons, as well as 4 litre, 1 litre, 250 mL aseptic cartons and 500 millilitre plastic jugs.
- China: Sweetened milk is a drink popular with students of all ages and is often sold in small plastic bags complete with straw. Adults not wishing to drink at a banquet often drink milk served from cartons or milk tea.
- Parts of Europe: Sizes of 500 millilitres, 1 litre (the most common), 1.5 litres, 2 litres and 3 litres are commonplace.
- Hong Kong - milk is sold in glass bottles (220 mL), cartons (236 mL and 1L), plastic jugs (2 litres) and aseptic cartons (250 mL).
- India and Pakistan: Commonly sold in 500 mL plastic bags. It is still customary to serve the milk boiled, despite pasteurization. Milk is often buffalo milk. Flavored milk is sold in most convenience stores in waxed cardboard containers. Convenience stores also sell many varieties of milk (such as flavored and ultra-pasteurized) in different sizes, usually in aseptic cartons.
- Indonesia: Usually sold in 1 litre cartons, but smaller, snack-sized cartons are available.
- Israel: Non-UHT milk is most commonly sold in 1 litre waxed cardboard boxes and 1 litre plastic bags. It may also be found in 0.5L and 2L waxed cardboard boxes, 2L plastic jugs and 1L plastic bottles. UHT milk is available in 1 litre (and less commonly also in 0.25L) carton "bricks".
- Japan: Commonly sold in 1 litre waxed cardboard boxes. In most city centers there is also home delivery of milk in glass jugs. As seen in China, sweetened and flavored milk drinks are commonly seen in vending machines.
- South Africa: Commonly sold in 1 litre bags. The bag is then placed in a plastic jug and the corner cut off before the milk is poured.
- South Korea: sold in cartons (180mL, 200mL, 500mL 900mL, 1L, 1.8L, 2.3L), plastic jugs (100Ml and 1.8L), aseptic cartons (180mL and 200mL) and plastic bags (100mL).
- Sweden: Commonly sold in 0.3 L, 1 L or 1.5 L cartons and sometimes as plastic or glass bottles..
- Poland: UHT milk is mostly sold in aseptic cartons (500mL, 1L, 2L), and non-UHT in 1L plastic bags or plastic bottles. Milk, UHT is commonly boiled, despite being pasteurized.
- Turkey: Commonly sold in 500 mL or 1L cartons or special plastic bottles. UHT milk is more popular. Milkmen also serve in smaller towns and villages.
- United Kingdom: Most stores still stock Imperial sizes: 1 pint (568 mL), 2 pints (1.136 L), 4 pints (2.273 L), 6 pints (3.408 L) or a combination including both metric and imperial sizes. Glass milk bottles delivered to the doorstep by the milkman are typically pint-sized and are returned empty by the householder for repeated reuse. Milk is also sold at supermarkets in either aseptic cartons or HDPE bottles. Milk can still be legally sold by the Imperial pint in reusable bottles in the UK under EU regulations (a distinction only shared with beer and cider), whilst a growing number of manufacturers such as Northern Foods now sell milk in 1 and 2 litre bottles.
- United States: Commonly sold in gallon (3.78 L), half-gallon (1.89 L) and quart (0.94 L) containers of rigid plastic or, occasionally for sizes less than a gallon, waxed cardboard, although bottles made of opaque PET are starting to become more commonplace in all smaller sizes. The US single-serving size is usually the half-pint (about 240 ml). Occasionally dairies will deliver milk straight to customers in coolers filled with glass bottles (usually half-gallon). Some convenience store chains in the United States (such as Kwik Trip in the Midwest) sell milk in 1/2 gallon bags.
- Uruguay: Commonly sold in 1 litre bags. The bag is then placed in a plastic jug and the corner cut off before the milk is poured.
Practically everywhere, condensed milk and evaporated milk is distributed in metal cans, 250 and 125 ml paper containers and 100 and 200 mL squeeze tubes, and powdered milk (skim and whole) is distributed in boxes or bags.

Spoilage and fermented milk products
When raw milk is left standing for a while, it turns "sour". This is the result of fermentation, where lactic acid bacteria ferment the lactose inside the milk into lactic acid. Prolonged fermentation may render the milk unpleasant to consume. This fermentation process is exploited by the introduction of bacterial cultures (e.g. Lactobacilli sp., Streptococcus sp., Leuconostoc sp., etc) to produce a variety of fermented milk products. The reduced pH from lactic acid accumulation denatures proteins and caused the milk to undergo a variety of different transformations in appearance and texture, ranging from an aggregate to smooth consistency. Some of these products include sour cream, yoghurt, cheese, buttermilk, viili, kefir and kumis. See Dairy product for more information.
Pasteurization of cow milk initially destroys any potential pathogens and increases the shelf-life [57][58], but eventually results in spoilage that makes it unsuitable for consumption. This causes it to assume an unpleasant odor, and the milk is deemed non-consumable due to unpleasant taste and an increased risk of food poisoning. In raw milk, the presence of lactic acid-producing bacteria, under suitable conditions, ferments the lactose present to lactic acid. The increasing acidity in turn prevents the growth of other organisms, or slows their growth significantly. During pasteurization however, these lactic acid bacteria are mostly destroyed.
In order to prevent spoilage, milk can be kept refrigerated and stored between 1 and 4 degrees Celsius in bulk tanks. Most milk is pasteurized by heating briefly and then refrigerated to allow transport from factory farms to local markets. The spoilage of milk can be forestalled by using ultra-high temperature (UHT) treatment; milk so treated can be stored unrefrigerated for several months until opened. Sterilized milk, which is heated for a much longer period of time, will last even longer, but also loses more nutrients and assume a different taste.[citation needed] Condensed milk, made by removing most of the water, can be stored in cans for many years, unrefrigerated, as can evaporated milk. The most durable form of milk is milk powder, which is produced from milk by removing almost all water. The moisture content is usually less than five percent in both drum and spray dried milk powder.
Language and culture
The importance of milk in human culture is attested to by the numerous expressions embedded in our languages, for example "the milk of human kindness". In ancient Greek mythology, the goddess Hera spilled her breast milk after refusing to feed Heracles, resulting in the Milky Way.
In African and Asian developing nations, butter is traditionally made from fermented milk rather than cream. It can take several hours of churning to produce workable butter grains from fermented milk.[59]
Holy books have also mentioned milk; the Bible contains references to the Land of Milk and Honey. In the Quran, there is a request to wonder on milk as follows: 'And surely in the livestock there is a lesson for you, We give you to drink of that which is in their bellies from the midst of digested food and blood, pure milk palatable for the drinkers.'(16-The Honeybee, 66). The Ramadhan fast is traditionally broken with a glass of milk and dates.
The verb, "to milk" something is often used in the vernacular of many English-speaking countries as a synonym for extortion or, in less loaded terms, taking advantage of a situation where one has another person at a disadvantage
The word milk has had many slang meanings over time. In the early 17th century the word was used to mean semen, or vaginal secretions, or to masturbate oneself or someone else. In the 19th century, milk was used to describe a cheap alcoholic drink made from methylated spirits mixed with water. The word was also used to mean defraud, to be idle, to intercept telegrams addressed to someone else, and a weakling. In the mid 1930s, the word was used in Australia meaning to siphon gas from a car. [60]
Milk is sometimes referred to as moo juice in American English,[61] while Cockney rhyming slang calls it Acker Bilk, Tom Silk, Lady in silk and Kilroy silk. [62]
The name of the Russian Molokan (Russian: "Молока́не") religion in Russian is derived from Russian "Молоко́ " meaning "Milk" as they would drink milk on the Russian Orthodox days of fast.
Other uses of milk
Besides serving as a beverage or source of food, milk is used by farmers and gardeners as an organic fungicide and foliage fertilizer. The potassium, fats, and salts naturally found in milk are absorbed by the leaves, which boost the plant's immune system, helping it to fight off diseases and fungi. Farmers, especially those who maintain grape vineyards, have tested a diluted milk solution in the past, and have found it to be more effective, yet less costly, than commercial products. Testing has also shown that it is unlikely to harm the plant that the solution is applied to. [63] [64]
See also
|
|
Notes
- ^ Comparison of the Cariogenicity of Cola, Honey, Cow Milk, Human Milk, and Sucrose
- ^ Soil pH: What it Means
- ^ . . . or just go with the flow?. The Times, May 5, 2005.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k McGee, Harold (1984). "Milk and Dairy Products". On Food and Cooking: The Science and Lore of the Kitchen. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 3–53. ISBN 0-684-18132-0.
- ^ news.bbc.co.uk : Early man couldn't stomach milk
- ^ Harvard Milk Days
- ^ "Moose milk makes for unusual cheese". The Globe and Mail. 26 June 2004. http://www.theglobeandmail.com/servlet/ArticleNews/TPStory/LAC/20040626/MOOSE26/TPEntertainment/Style. Retrieved on 2007-08-27.
- ^ FAO Food outlook: International dairy product prices are turning down: how far, how fast? FAO online publication, 1 June 2006
- ^ "A Thirst for Milk Bred by New Wealth Sends Prices Soaring" article by Wayne Arnold in the New York Times September 4, 2007
- ^ Dairy Chemistry and Physics, webpage of University of Guelph
- ^ Dairy Chemistry and Physics, webpage of University of Guelph
- ^ Homogenization of Milk and Milk Products, webpage of University of Guelph
- ^ "Research Can Lead To Longer Shelf Life For Dairy Products"
- ^ a b "Does homogenization affect the human health properties of cow’s milk?"
- ^ http://herbalwhirled.blogspot.com/2006/11/pasteurized-homogenized-milk-and-your.html
- ^ Introduction to Dairy Science and Technology, webpage of University of Guelph
- ^ Milk contains traces of ash
- ^ Milk From Cows and Other Animals, web page by Washington Dairy Products Commission
- ^ MSN encarta
- ^ Morales, Edmundo (1995). The Guinea Pig : Healing, Food, and Ritual in the Andes. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 0-8165-1558-1.
- ^ Jones, Alicia Noelle (2002). "Density of Milk". The Physics Factbook. http://hypertextbook.com/facts/2002/AliciaNoelleJones.shtml.
- ^ Calcium Rich Foods: Get All The Calcium You Need Without Milk
- ^ Feskanich D, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA. Milk, dietary calcium, and bone fractures in women: a 12-year prospective study. Am J Public Health 1997; 87:992-7.
- ^ Brody T. Calcium and phosphate. In: Nutritional biochemistry. 2nd ed. Boston: Academic Press, 1999:761–94
- ^ American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Heaney and Weaver, 51 (4): 656.
- ^ Dairy's Role in Managing Blood Pressure, web page of the US National Dairy Council
- ^ Fat ice cream and milk may help woman shoot for pregnancy - Pravda.Ru
- ^ Cow's milk protein allergy and intolerance in infa...[Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1994] - PubMed Result
- ^ Reichelt KL, Knivsberg A-M, Lind G, Nødland M (1991). "Probable etiology and possible treatment of childhood autism". Brain Dysfunct 4: 308–19.
- ^ a b Christison GW, Ivany K (2006). "Elimination diets in autism spectrum disorders: any wheat amidst the chaff?". J Dev Behav Pediatr 27 (2 Suppl 2): S162. doi:. PMID 16685183.
- ^ Hakkak, et al., "Dietary Whey Protein Protects against Azoxymethane-induced Colon Tumors in Male Rats," Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention, Vol. 10, 555-558, May 2001.
- ^ a b H. Chen et al., Consumption of Dairy Products and Risk of Parkinson's Disease, American Journal of Epidemiology. 2007 May;165(9):998-1006
- ^ "Milk linked to Parkinson's risk". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/4419477.stm.
- ^ Giovannucci, E. et al., Calcium and fructose intake in relation to risk of prostate cancer., Cancer Res. 1998 Feb 1;58(3):442-7.
- ^ http://yedda.com/questions/Low_fat_milk_causes_prostate_cancer_7351021963170/
- ^ Chan, J.M., Dairy products, calcium, and prostate cancer risk in the Physicians' Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001 Oct;74(4):549-54. (disputed publication)
- ^ The World Cancer Research Fund and American Institute for Cancer Research (1997). "Food, nutrition and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective". Food, nutrition and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective.
- ^ Chan JM et al., (2005) Role of diet in prostate cancer development and progression. J Clin Oncol 23:8152-60.
- ^ How Bacteria In Cows' Milk May Cause Crohn's Disease
- ^ Cow milk protein allergy presenting with Hirschsprung's disease–mimicking symptoms.
- ^ Humoral and cell mediated immune response to cow's milk proteins in Behçet's disease
- ^ Kahan, Z et al., Elevated levels of circulating insulin-like growth factor-I, IGF-binding globulin-3 and testosterone predict hormone-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal women: a case-control study. Int J Oncol. 2006 Jul;29(1):193-200.
- ^ Pacher, M. et al., Impact of constitutive IGF1/IGF2 stimulation on the transcriptional program of human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2006 Jun 14
- ^ IDFA - Biotechnology and Bovine Somatotropin (BST or BGH)
- ^ International Scientific Committee Warns of Serious Risks of Breast and Prostate Cancer from Monsanto's Hormonal Milk. Press release of the Cancer Prevention Coalition.
- ^ Oca News Articles
- ^ Dietary IGF-I and rbST
- ^ Milk: Epstein, S., America's Health Problem. Web page of the Cancer Prevention Coalition.
- ^ Mastitis Control Programs: Milk Quality Evaluation Tools for Dairy Farmers
- ^ Greger, Michael. Paratuberculosis and Crohn's Disease: Got Milk? Pro-vegan online publication, January 2001
- ^ Paratuberculosis and Crohn's Disease: Got Milk? (Vegan Outreach)
- ^ McGee, Harold (2004). On Food and Cooking: The Science and Lore of the Kitchen, Completely Revised and Updated. New York, NY: Scribner. pp. 13. ISBN 9780684800011.
- ^ Google Books - Designing Foods: Animal Product Options in the Marketplace
- ^ "How to Buy Dairy Products", Home and Garden Bulletin 255, USDA, February 1995. Retrieved 16 May 2007.
- ^ "Yogurt and Other Cultured Dairy Products", National Dairy Council, 2000.
- ^ Rombauer, Irma S. and Marion Rombauer Becker (1975). Joy of Cooking (Revised Edition). Bobbs Merrill. pp. 533. ISBN 0-672-51831-7.
- ^ Got Milk? Make Sure It's Pasteurized
- ^ Shelf-Life of Pasteurized Fluid Milk as Affected by Age of Raw Milk
- ^ Crawford et al, part B, section III, ch. 1: Butter. Retrieved 28 November 2005.
- ^ Cassell's Dictionary of Slang
- ^ MILK, MOO JUICE and AMERICAN ENGLISH
- ^ Cockney Rhyming Slang
- ^ "Drop of white the right stuff for vines". Science Daily. 2002-09-12. http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2002/09/020912071438.htm. Retrieved on 2009-04-01.
- ^ Campbell, Malcom (2003-09-19). "Fact Sheet: Milk Fungicide". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. http://www.abc.net.au/gardening/stories/s948323.htm. Retrieved on 2009-04-01.
References
- McGee, Harold (2004). On Food and Cooking (Revised Edition). Scribner. ISBN 0-684-80001-2.
- Information on milk by Parmalat
- Introduction to Dairy Science and Technology: Milk History, Consumption, Production, and Composition
- Milk
- Milk Notes
External links
| Wikibooks Cookbook has a recipe/module on |
| Look up milk in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Milk |
- Harvard School of Public Health: Calcium and Milk: describes claims of milk supporters and critics