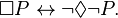Modal logic
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding reliable references (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (August 2008) |
A modal logic is any system of formal logic that attempts to deal with modalities. Modals qualify the truth of a judgment. Traditionally, there are three "modes" or "moods" or "modalities" represented by modal logic, namely, possibility, probability, and necessity. Logics for dealing with a number of related terms, such as eventually, formerly, can, could, might, may, must, are by extension also called modal logics, since it turns out that these can be treated in similar ways.
A formal modal logic represents modalities using modal operators. For example, "It might rain today" and "It is possible that rain will fall today" both contain the notion of possibility. In a modal logic this is represented as an operator, Possibly, attached to the sentence It will rain today.
The basic unary (1-place) modal operators are usually written  (or L) for Necessarily and
(or L) for Necessarily and  (or M) for Possibly. In a classical modal logic, each can be expressed by the other and negation:
(or M) for Possibly. In a classical modal logic, each can be expressed by the other and negation:
Thus it is possible that it will rain today if and only if it is not necessary that it will not rain today. For the standard formal semantics of the basic modal language, see Kripke semantics.
Contents |
[edit] Brief history
In 1918 C.I. Lewis introduced a formal axiomatic modal logic system, acknowledging the use of the ideas of Hugh Brown from the 1890s. In 1932 C.I. Lewis and Cooper H. Langford introduced the systems S1 through S5 (with S3 being the original system proposed in C.I. Lewis's 1918 work). By the late 1930s many systems were known. Major changes in how the systems were viewed were later provided by Kurt Gödel (use of "Necessity" as primitive, and PC+axioms) and Saul Kripke (a reasonable semantics for most, but not all, modal logics).
[edit] Alethic modalities
Modalities of necessity and possibility are called alethic modalities. They are also sometimes called special modalities, from the Latin species. Modal logic was first developed to deal with these concepts, and only afterward was extended to others. For this reason, or perhaps for their familiarity and simplicity, necessity and possibility are often casually treated as the subject matter of modal logic. Moreover it is easier to make sense of relativizing necessity, e.g. to legal, physical, nomological, epistemic, and so on, than it is to make sense of relativizing other notions.
A proposition is said to be
- possible if and only if it is not necessarily false (regardless of whether it is actually true or actually false);
- necessary if and only if it is not possibly false; and
- contingent if and only if it is not necessarily false and not necessarily true (ie. possible but not necessary).
Clearly if we wish the definitions of these notions to be non-circular, we need to take either possibility or necessity as primitive.
[edit] Physical possibility
Something is physically possible if it is permitted by the laws of physics. For example, current theory allows for there to be an atom with an atomic number of 150, though there may not in fact be one. On the other hand, it is not possible for there to be an atom whose nucleus contains cheese. While it is logically possible to accelerate beyond the speed of light, that is not, according to modern science, physically possible for material particles or information.
[edit] Metaphysical possibility
Philosophers ponder the properties that objects have independently of those dictated by scientific laws. For example, it might be metaphysically necessary, as some have thought, that all thinking beings have bodies and can experience the passage of time, or that God exists. Saul Kripke has argued that every person necessarily has the parents they do have: anyone with different parents would not be the same person.
Metaphysical possibility is generally thought to be more restricting than bare logical possibility (i.e., fewer things are metaphysically possible than are logically possible). Its exact relation to physical possibility is a matter of some dispute. Philosophers also disagree over whether metaphysical truths are necessary merely "by definition", or whether they reflect some underlying deep facts about the world, or something else entirely.
[edit] Confusion with epistemic modalities
Alethic modalities and epistemic modalities (see below) are often expressed in English using the same words. "It is possible that bigfoot exists" can mean either "Bigfoot could exist, whether or not bigfoot does in fact exist" (alethic), or more likely, "For all I know, bigfoot exists" (epistemic).
[edit] Epistemic logic
Epistemic modalities (from the Greek episteme, knowledge), deal with the certainty of sentences. The  operator is translated as "x knows that...", and the
operator is translated as "x knows that...", and the  operator is translated as "For all x knows, it may be true that..." In ordinary speech both metaphysical and epistemic modalities are often expressed in similar words; the following contrasts may help:
operator is translated as "For all x knows, it may be true that..." In ordinary speech both metaphysical and epistemic modalities are often expressed in similar words; the following contrasts may help:
A person, Jones, might reasonably say both: (1) "No, it is not possible that Bigfoot exists; I am quite certain of that"; and, (2) "Sure, Bigfoot possibly could exist". What Jones means by (1) is that given all the available information, there is no question remaining as to whether Bigfoot exists. This is an epistemic claim. By (2) he makes the metaphysical claim that it is possible for Bigfoot to exist, even though he does not (which is not equivalent to "it is possible that Bigfoot exists – for all I know," which contradicts (1)).
From the other direction, Jones might say, (3) "It is possible that Goldbach's conjecture is true; but also possible that it is false", and also (4) "if it is true, then it is necessarily true, and not possibly false". Here Jones means that it is epistemically possible that it is true or false, for all he knows (Goldbach's conjecture has not been proven either true or false), but if there is a proof (heretofore undiscovered), then it would show that it is not logically possible for Goldbach's conjecture to be false—there could be no set of numbers that violated it. Logical possibility is a form of alethic possibility; (4) makes a claim about whether it is possible (ie, logically speaking) that a mathematical truth to have been false, but (3) only makes a claim about whether it is possible, for all Jones knows, (ie, speaking of certitude) that the mathematical claim is specifically either true or false, and so again Jones does not contradict himself. It is worthwhile to observe that Jones is not necessarily correct: It is possible (epistemically) that Goldbach's conjecture is both true and unprovable.[1]
Epistemic possibilities also bear on the actual world in a way that metaphysical possibilities do not. Metaphysical possibilities bear on ways the world might have been, but epistemic possibilities bear on the way the world may be (for all we know). Suppose, for example, that I want to know whether or not to take an umbrella before I leave. If you tell me "it is possible that it is raining outside" – in the sense of epistemic possibility – then that would weigh on whether or not I take the umbrella. But if you just tell me that "it is possible for it to rain outside" – in the sense of metaphysical possibility – then I am no better off for this bit of modal enlightenment.
Some features of epistemic modal logic are in debate. For example, if x knows that p, does x know that it knows that p? That is to say, should  be an axiom in these systems? While the answer to this question is unclear, there is at least one axiom that must be included in epistemic modal logic, because it is minimally true of all modal logics (see the section on axiomatic systems):
be an axiom in these systems? While the answer to this question is unclear, there is at least one axiom that must be included in epistemic modal logic, because it is minimally true of all modal logics (see the section on axiomatic systems):
- K, Distribution Axiom:
 .
.
But this is disconcerting, because with K, we can prove that we know all the logical consequences of our beliefs: If q is a logical consequence of p, then 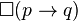 . And if so, then we can deduce that
. And if so, then we can deduce that 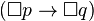 using K. When we translate this into epistemic terms, this says that if q is a logical consequence of p, then we know that it is, and if we know p, we know q. That is to say, we know all the logical consequences of our beliefs. This must be true for all possible modal interpretations of epistemic cases where
using K. When we translate this into epistemic terms, this says that if q is a logical consequence of p, then we know that it is, and if we know p, we know q. That is to say, we know all the logical consequences of our beliefs. This must be true for all possible modal interpretations of epistemic cases where  is translated as "knows that." But then, for example, if x knows that prime numbers are divisible only by themselves and the number one, then x knows that 8683317618811886495518194401279999999 is prime (since this number is only divisible by itself and the number one). That is to say, under the modal interpretation of knowledge, anyone who knows the definition of a prime number knows that this number is prime. This shows that epistemic modal logic is an idealized account of knowledge, and explains objective, rather than subjective knowledge (if anything).
is translated as "knows that." But then, for example, if x knows that prime numbers are divisible only by themselves and the number one, then x knows that 8683317618811886495518194401279999999 is prime (since this number is only divisible by itself and the number one). That is to say, under the modal interpretation of knowledge, anyone who knows the definition of a prime number knows that this number is prime. This shows that epistemic modal logic is an idealized account of knowledge, and explains objective, rather than subjective knowledge (if anything).
[edit] Temporal logic
Temporal modal logic takes advantage of the fact that propositions are true or false in time. So '2 + 2 = 4' is true at all times, while 'John is happy' is only true at some times.
A standard method for formalizing talk of time is to use two pairs of operators, one for the past and one for the future (P will just mean 'it is presently the case that P'). For example:
- FP : It will sometime be the case that P
- GP : It will always be the case that P
- PP : It was sometime the case that P
- HP : It has always been the case that P
There are then at least three modal logics that we can develop. For example, we can stipulate that,
 = P is the case at some time t
= P is the case at some time t = P is the case at every time t
= P is the case at every time t
and we can add two other operators to talk about the future by itself (these would have to be distinguished from the first set by some subscript). Either,
 = FP
= FP = GP
= GP
or,
 = P and/or FP
= P and/or FP = P and GP
= P and GP
The second and third interpretations may seem odd, but such assignments do create modal systems. Note that FP is the same as ¬G¬P. We can combine the above operators to form complex statements. For example, PP →  PP says (effectively), Everything that is past and true is necessary.
PP says (effectively), Everything that is past and true is necessary.
It seems reasonable to say that possibly it will rain tomorrow, and possibly it won't; on the other hand, seeing as how we can't change the past, if it rained yesterday, it probably isn't true that it may not have rained yesterday. It seems the past is "fixed", or necessary, in a way the future is not. This is sometimes referred to as accidental necessity. But if the past is "fixed", and everything that is in the future will eventually be in the past, then it seems plausible to say that future events are necessary too. Philosophers have worked out various ways of dealing with this problem of future contingents.
Additional binary operators are also relevant to temporal logics, q.v. Linear Temporal Logic.
[edit] Deontic logic
Likewise talk of morality, or of obligation and norms generally, seems to have a modal structure. The difference between "You must do this" and "You may do this" looks a lot like the difference between "This is necessary" and "This is possible". Such logics are called deontic, from the Greek for "duty". One characteristic feature of deontic logics is that they lack the axiom T semantically corresponding to the reflexivity of the accessibility relation in Kripke semantics: in symbols,  . Interpreting
. Interpreting  as "it is obligatory that", T informally says that every obligation is true. For example, if it is obligatory not to kill others (i.e. killing is morally forbidden), then T implies that people actually do not kill others. This consequence is obviously false.
as "it is obligatory that", T informally says that every obligation is true. For example, if it is obligatory not to kill others (i.e. killing is morally forbidden), then T implies that people actually do not kill others. This consequence is obviously false.
However, in Kripke semantics for deontic logic, T is supposed to hold at accessible worlds (relative to the actual world w). These worlds are to be thought of as idealized in the sense that all obligations (in w) are fulfilled there. Hence a sentence A is obligatory just in case A holds at all idealized worlds. So in order to discuss obligations under Kripke semantics, there must be some world where  , where everything that ought to be the case, is the case. Though this was one of the first interpretations of the formal semantics, it has recently come under criticism. See e.g. Sven Hansson, "Ideal Worlds--Wishful Thinking in Deontic Logic", Studia Logica, Vol. 82 (3), pp. 329-336, 2006.
, where everything that ought to be the case, is the case. Though this was one of the first interpretations of the formal semantics, it has recently come under criticism. See e.g. Sven Hansson, "Ideal Worlds--Wishful Thinking in Deontic Logic", Studia Logica, Vol. 82 (3), pp. 329-336, 2006.
One other principle that is often (at least traditionally) accepted as a deontic principle is D, 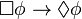 , which corresponds to the seriality (or extendability or unboundedness) of the accessibility relation. It is an embodiment of the Kantian idea that "ought implies can". (Clearly the "can" can be interpreted in various senses, e.g. in a moral or alethic sense.)
, which corresponds to the seriality (or extendability or unboundedness) of the accessibility relation. It is an embodiment of the Kantian idea that "ought implies can". (Clearly the "can" can be interpreted in various senses, e.g. in a moral or alethic sense.)
[edit] Intuitive problems with deontic logic
When we try and formalize ethics with standard modal logic, we run into some problems. Suppose that we have a proposition K: you kill the victim, and another, Q: you kill the victim quickly. Now suppose we want to express the thought that "if you do kill the victim, you ought to kill him quickly." There are two likely candidates,
- (1)

- (2)

But (1) says that if you kill the victim, then it ought to be the case that you kill him quickly. This surely isn't right, because you ought not to have killed him at all. And (2) doesn't work either. If the right representation of "if you kill the victim then you ought to kill him quickly" is (2), then the right representation of (3) "if you kill the victim then you ought to kill him slowly" is 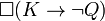 . Now suppose (as seems reasonable) that you should not kill the victim, or
. Now suppose (as seems reasonable) that you should not kill the victim, or 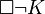 . Then we can deduce
. Then we can deduce 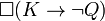 using the principle of explosion and the minimally true K axiom, which would express sentence (3). So if you should not kill the victim, then if you kill him, you should kill him slowly. But that can't be right, and is not right when we use natural language. Telling someone they should not kill the victim certainly does not imply that they should kill the victim slowly if they do kill him.[2]
using the principle of explosion and the minimally true K axiom, which would express sentence (3). So if you should not kill the victim, then if you kill him, you should kill him slowly. But that can't be right, and is not right when we use natural language. Telling someone they should not kill the victim certainly does not imply that they should kill the victim slowly if they do kill him.[2]
[edit] Doxastic logic
Doxastic logic concerns the logic of belief (of some set of agents). The term doxastic is derived from the ancient Greek doxa which means "belief." Typically, a doxastic logic uses  , often written "B", to mean "It is believed that", or when relativized to a particular agent s, "It is believed by s that".
, often written "B", to mean "It is believed that", or when relativized to a particular agent s, "It is believed by s that".
[edit] Other modal logics
Significantly, modal logics can be developed to accommodate most of these idioms; it is the fact of their common logical structure (the use of "intensional" or non-truth-functional sentential operators) that make them all varieties of the same thing.
[edit] Interpretations of modal logic
In the most common interpretation of modal logic, one considers "all logically possible worlds". If a statement is true in all possible worlds, then it is a necessary truth. If a statement happens to be true in our world, but is not true in all possible worlds, then it is a contingent truth. A statement that is true in some possible world (not necessarily our own) is called a possible truth.
Whether this "possible worlds idiom" is the best way to interpret modal logic, and how literally this idiom can be taken, is a live issue for metaphysicians. For example, the possible worlds idiom would translate the claim about Bigfoot as "There is some possible world in which Bigfoot exists". To maintain that Bigfoot's existence is possible, but not actual, one could say, "There is some possible world in which Bigfoot exists; but in the actual world, Bigfoot does not exist". But it is unclear what it is that making modal claims commits us to. Are we really alleging the existence of possible worlds, every bit as real as our actual world, just not actual? David Lewis made himself notorious by biting the bullet, asserting that all merely possible worlds are as real as our own, and that what distinguishes our world as actual is simply that it is indeed our world – this world (see Indexicality). That position is a major tenet of "modal realism". Most philosophers decline to endorse such a view, considering it ontologically extravagant, and preferring to seek various ways to paraphrase away these ontological commitments.
[edit] Axiomatic Systems
Many systems of modal logic, with widely varying properties, have been proposed since C. I. Lewis began working in the area in 1910. Hughes and Cresswell (1996), for example, describe 42 normal and 25 non-normal modal logics. Zeman (1973) describes some systems Hughes and Cresswell omit.
Modern treatments of modal logic begin by augmenting the propositional calculus with two unary operations, one denoting "necessity" and the other "possibility". The notation of Lewis, much employed since, denotes "necessarily p" by a prefixed "box" ( 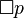 ) whose scope is established by parentheses. Likewise, a prefixed "diamond" (
) whose scope is established by parentheses. Likewise, a prefixed "diamond" ( ) denotes "possibly p". Regardless of notation, each of these operators is definable in terms of the other:
) denotes "possibly p". Regardless of notation, each of these operators is definable in terms of the other:
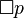 (necessarily p) is equivalent to
(necessarily p) is equivalent to  ("not possible that not-p")
("not possible that not-p") (possibly p) is equivalent to
(possibly p) is equivalent to 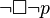 ("not necessarily not-p")
("not necessarily not-p")
Hence  and
and  form a dual pair of operators.
form a dual pair of operators.
In many modal logics, the necessity and possibility operators satisfy the following analogs of de Morgan's laws from Boolean algebra:
- "It is not necessary that X" is logically equivalent to "It is possible that not X".
- "It is not possible that X" is logically equivalent to "It is necessary that not X".
Precisely what axioms and rules must be added to the propositional calculus to create a usable system of modal logic is a matter of philosophical opinion, often driven by the theorems one wishes to prove. Many modal logics, known collectively as normal modal logics, include the following rule and axiom:
- N, Necessitation Rule: If p is a theorem (of any system invoking N), then
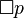 is likewise a theorem.
is likewise a theorem. - K, Distribution Axiom:
 .
.
The weakest normal modal logic, named K in honor of Saul Kripke, is simply the propositional calculus augmented by  , the rule N, and the axiom K. K is weak in that it fails to determine whether a proposition can be necessary but only contingently necessary. That is, it is not a theorem of K that if
, the rule N, and the axiom K. K is weak in that it fails to determine whether a proposition can be necessary but only contingently necessary. That is, it is not a theorem of K that if 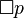 is true then
is true then  is true, i.e., that necessary truths are "necessarily necessary". If such perplexities are deemed forced and artificial, this defect of K is not a great one. In any case, different answers to such questions yield different systems of modal logic.
is true, i.e., that necessary truths are "necessarily necessary". If such perplexities are deemed forced and artificial, this defect of K is not a great one. In any case, different answers to such questions yield different systems of modal logic.
Adding axioms to K gives rise to other well-known modal systems. One cannot prove in K that if "p is necessary" then p is true. The axiom T remedies this defect:
- T, Reflexivity Axiom:
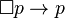 (If p is necessary, then p is the case.) T holds in most but not all modal logics. Zeman (1973) describes a few exceptions, such as S10.
(If p is necessary, then p is the case.) T holds in most but not all modal logics. Zeman (1973) describes a few exceptions, such as S10.
Other well-known elementary axioms are:
- 4:

- B:

- D:

- E:
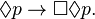
These axioms yield the systems:
- K := K + N
- T := K + T
- S4 := T + 4
- S5 := S4 + B or T + E
- D := K + D.
K through S5 form a nested hierarchy of systems, making up the core of normal modal logic. But specific rules or sets of rules may be appropriate for specific systems. For example, in deontic logic,  (If it ought to be that P, then it is permitted that P) seems appropriate, but we should probably not include that
(If it ought to be that P, then it is permitted that P) seems appropriate, but we should probably not include that  .
.
The commonly employed system S5 simply makes all modal truths necessary. For example, if p is possible, then it is "necessary" that p is possible. Also, if p is necessary, then it is necessary that p is necessary. Although controversial, this is commonly justified on the grounds that S5 is the system obtained if every possible world is possible relative to every other world. Other systems of modal logic have been formulated, in part because S5 does not describe every kind of metaphysical modality of interest. This suggests that talk of possible worlds and their semantics may not do justice to all modalities.
[edit] Development of modal logic
Although Aristotle's logic is almost entirely concerned with the theory of the categorical syllogism, there are passages in his work, such as the famous Sea-Battle Argument in De Interpretatione § 9, that are now seen as anticipations of modal logic and its connection with potentiality and time. Modal logic as a self-aware subject owes much to the writings of the Scholastics, in particular William of Ockham and John Duns Scotus, who reasoned informally in a modal manner, mainly to analyze statements about essence and accident.
C. I. Lewis founded modern modal logic in his 1910 Harvard thesis and in a series of scholarly articles beginning in 1912. This work culminated in his 1932 book Symbolic Logic (with C. H. Langford), which introduced the five systems S1 through S5. The contemporary era in modal logic began in 1959, when Saul Kripke (then only a 19 year old Harvard University undergraduate) introduced the now-standard Kripke semantics for modal logics. These are commonly referred to as "possible worlds" semantics. Kripke and A. N. Prior had previously corresponded at some length.
A. N. Prior created temporal logic, closely related to modal logic, in 1957 by adding modal operators [F] and [P] meaning "henceforth" and "hitherto". Vaughan Pratt introduced dynamic logic in 1976. In 1977, Amir Pnueli proposed using temporal logic to formalise the behaviour of continually operating concurrent programs. Flavors of temporal logic include propositional dynamic logic (PDL), propositional linear temporal logic (PLTL), linear temporal logic (LTL), computational tree logic (CTL), Hennessy-Milner logic, and T.
The mathematical structure of modal logic, namely Boolean algebras augmented with unary operations (often called "modal algebras"), began to emerge with J. C. C. McKinsey's 1941 proof that S2 and S4 are decidable, and reached full flower in the work of Alfred Tarski and his student Bjarni Jonsson (Jonsson and Tarski 1951-52). This work revealed that S4 and S5 are models of interior algebra, a proper extension of Boolean algebra originally designed to capture the properties of the interior and closure operators of topology. Texts on modal logic typically do little more than mention its connections with the study of Boolean algebras and topology. For a thorough survey of the history of formal modal logic and of the associated mathematics, see Goldblatt (2006).
[edit] References
- Blackburn, Patrick; de Rijke, Maarten; and Venema, Yde (2001) Modal Logic. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-80200-8
- Blackburn, P.; van Benthem, J.; and Wolter, Frank; Eds. (2006) Handbook of Modal Logic. North Holland.
- Chagrov, Aleksandr; and Zakharyaschev, Michael (1997) Modal Logic. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-853779-4
- Chellas, B. F. (1980) Modal Logic: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-22476-4
- Cresswell, M. J. (2001) "Modal Logic" in Goble, Lou; Ed., The Blackwell Guide to Philosophical Logic. Basil Blackwell: 136-58. ISBN 0-631-20693-0
- Fitting, Melvin; and Mendelsohn, R. L. (1998) First Order Modal Logic. Kluwer. ISBN 0-7923-5335-8
- Garson, James W. (2006) Modal Logic for Philosophers. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-68229-0. A thorough introduction to modal logic, with coverage of various derivation systems and a distinctive approach to the use of diagrams in aiding comprehension.
- Girle, Rod (2000) Modal Logics and Philosophy. Acumen (UK). ISBN 0-7735-2139-9. Proof by refutation trees. A good introduction to the varied interpretations of modal logic.
- Goldblatt, Robert (1992) "Logics of Time and Computation", 2nd ed., CSLI Lecture Notes No. 7. University of Chicago Press.
- —— (1993) Mathematics of Modality, CSLI Lecture Notes No. 43. University of Chicago Press.
- —— (2006) "Mathematical Modal Logic: a View of its Evolution," in Gabbay, D. M.; and Woods, John; Eds., Handbook of the History of Logic, Vol. 6. Elsevier BV.
- Goré, Rajeev (1999) "Tableau Methods for Modal and Temporal Logics" in D'Agostino, M.; Gabbay, Dov; Haehnle, R.; and Posegga, J.; Eds., Handbook of Tableau Methods. Kluwer: 297-396.
- Hughes, G. E., and Cresswell, M. J. (1996) A New Introduction to Modal Logic. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-12599-5
- Jónsson, B. and Tarski, A., 1951-52, "Boolean Algebra with Operators I and II", American Journal of Mathematics 73: 891-939 and 74: 129-62.
- Kracht, Marcus (1999) Tools and Techniques in Modal Logic, Studies in Logic and the Foundations of Mathematics No. 142. North Holland.
- Lemmon, E. J. (with Scott, D.) (1977) An Introduction to Modal Logic, American Philosophical Quarterly Monograph Series, no. 11 (Krister Segerberg, series ed.). Basil Blackwell.
- Lewis, C. I. (with Langford, C. H.) (1932). Symbolic Logic. Dover reprint, 1959.
- Prior, A. N. (1957) Time and Modality. Oxford University Press.
Free and online:
- Zeman, J. J. (1973) Modal Logic. Reidel. Employs Polish notation.
[edit] See also
[edit] Notes
- ^ See Goldbach's conjecture > Origins
- ^ Ted Sider's Logic for Philosophy Currently page 228, but subject to change.
[edit] External links
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy:
- "Modal logic" – by James Garson.
- "Provability Logic" – by Rineke Verbrugge.
- Edward N. Zalta, 1995, "Basic Concepts in Modal Logic."
- John McCarthy, 1996, "Modal Logic."
- Molle a Java prover for experimenting with modal logics
- Suber, Peter, 2002, "Bibliography of Modal Logic."
- List of Logic Systems List of many modal logics with sources, by John Halleck.
- Advances in Modal Logic. Biannual international conference and book series in modal logic.
[edit] Acknowledgements
This article includes material from the Free On-line Dictionary of Computing, used with permission under the GFDL.