Montreal
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| City of Montreal Ville de Montréal |
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto: Concordia Salus ("well-being through harmony") | |||||
| Location of Montreal in Quebec | |||||
| Coordinates: | |||||
| Country | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province | |||||
| Region | Montréal | ||||
| Founded | 1642 | ||||
| Established | 1832 | ||||
| Government | |||||
| - Mayor | Gérald Tremblay | ||||
| - Language | French (official) | ||||
| Area [1][2][3] | |||||
| - City | 365.13 km2 (140.98 sq mi) | ||||
| - Urban | 1,677 km2 (647 sq mi) | ||||
| - Metro | 4,259 km2 (1,644 sq mi) | ||||
| Highest elevation | 233 m (764 ft) | ||||
| Lowest elevation | 6 m (20 ft) | ||||
| Population (2006)[1][2][3] | |||||
| - City | 1,620,693 (ranked 2nd) | ||||
| - Density | 4,439/km2 (11,496/sq mi) | ||||
| - Urban | 3,316,615 | ||||
| - Metro | 3,635,571 | ||||
| - Demonym | Montrealer (English), Montréalais / Montréalaise (French) | ||||
| Time zone | Eastern (EST) (UTC-5) | ||||
| - Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC-4) | ||||
| Postal code span | H | ||||
| Area code(s) | (514) and (438) | ||||
| Website | Ville de Montréal | ||||
Montreal, or Montréal,[4] (pronounced ![]() [mɔ̃ʁeˈal] (help·info) in French,
[mɔ̃ʁeˈal] (help·info) in French, ![]() /ˌmʌntriˈɑːl/ (help·info) in English) is the largest city in the Canadian province of Quebec and the second-largest city in Canada. Montreal was the largest city in Canada up until 1976 when it was surpassed in size by Toronto.[5] Originally called Ville-Marie ('City of Mary'),[6] the city takes its present name from Mount Royal, the three-headed hill at the heart of the city, whose name was also initially given to the island on which the city is located,[7][8] or Mont Réal as it was spelt in Middle French,[9] (Mont Royal / in present French).
/ˌmʌntriˈɑːl/ (help·info) in English) is the largest city in the Canadian province of Quebec and the second-largest city in Canada. Montreal was the largest city in Canada up until 1976 when it was surpassed in size by Toronto.[5] Originally called Ville-Marie ('City of Mary'),[6] the city takes its present name from Mount Royal, the three-headed hill at the heart of the city, whose name was also initially given to the island on which the city is located,[7][8] or Mont Réal as it was spelt in Middle French,[9] (Mont Royal / in present French).
The official language of Montreal is French as defined by the city's charter.[10][11] Montreal is the second-largest primarily French-speaking city in the world, after Paris.[12] As of the 2006 Canadian Census, 1,620,693 people resided in the city of Montreal proper.[1] The population of the Montreal Census Metropolitan Area (also known as Greater Montreal) was 3,635,571 at the same 2006 census. In the census metropolitan area, French is the language most spoken at home by 70.5% of the population (as of 2006 census).[13]
Contents |
[edit] History
There is archaeological evidence of various nomadic native peoples occupying the island of Montreal for at least 2,000 years before the arrival of Europeans.[14] The St. Lawrence Iroquoians established the village of Hochelaga at the foot of Mount Royal.[15] The French explorer Jacques Cartier visited Hochelaga on October 2, 1535, claiming the St. Lawrence Valley for France.[16] He estimated the population to be "over a thousand".[15]
Seventy years later, French explorer Samuel de Champlain reported that the St. Lawrence Iroquoians and their settlements had disappeared altogether from the St. Lawrence valley, likely due to inter-tribal wars, European diseases and out-migration.[15] Champlain established in 1611 a fur trading post on the Island of Montreal, on a site initially named La Place Royale, at the confluence of Saint-Pierre River and St. Lawrence River, where present-day Pointe-à-Callière stands.[17] In 1639, Jérôme Le Royer de La Dauversière obtained the Seigneurial title to the Island of Montreal in the name of the Société de Notre-Dame de Montréal to establish a Roman Catholic mission for evangelizing natives. Paul Chomedey de Maisonneuve was the governor of the colony.[18]
Ville-Marie became a centre for the fur trade and a base for further French exploration in North America.[18] It remained a French colony until 1760, when it was surrendered to Great Britain.[19]
Montreal was incorporated as a city in 1832.[20] The opening of the Lachine Canal permitted ships to bypass the unnavigable Lachine Rapids,[21] while the construction of the Victoria Bridge established Montreal as a major railway hub. By 1860, it was the largest city in British North America and the undisputed economic and cultural centre of Canada.[22][23]
Montreal was the capital of the Province of Canada from 1844 to 1849, but lost its status when a Tory mob burnt down the Parliament building to protest the passage of the Rebellion Losses Bill.[24]
After World War I, the Prohibition movement in the United States turned Montreal into a haven for Americans looking for alcohol.[25] Unemployment remained high in the city, and was exacerbated by the Stock Market Crash of 1929 and the Great Depression.[26]
During World War II, Mayor Camillien Houde protested against conscription and urged Montrealers to disobey the federal government's registry of all men and women.[27] Ottawa was furious over Houde's insubordination and held him in a prison camp until 1944,[28] when the government was forced to institute conscription (see Conscription Crisis of 1944).[27]
By 1951, Montreal's population had surpassed one million people.[29] The Saint Lawrence Seaway opened in 1959, allowing vessels to bypass Montreal: a development that would in time help to spell the end of the city's economic dominance.[30] However, the 1960s saw continued growth, including Expo 67, the construction of Canada's tallest skyscrapers, new expressways and the Montreal Metro system.
The 1970s ushered in a period of wide-ranging social and political changes, stemming in large part from the concerns of the French-Canadian majority about the conservation of their culture and language, given the traditional predominance of the English-Canadian minority in the business arena.[31] The October Crisis and the election of the separatist political party, the Parti Québécois, resulted in the departure of many businesses and people from the city.[32] In 1976, Montreal was the host of the 1976 Summer Olympics.[33]
During the 1980s and early 1990s, Montreal experienced a slower rate of economic growth than many other major Canadian cities. By the late 1990s, however, Montreal's economic climate had improved, as new firms and institutions began to fill the traditional business and financial niches.
Montreal was merged with the 27 surrounding municipalities on the Island of Montreal on January 1, 2002. The merger created a unified city of Montreal which covered the entire island of Montreal. This move proved unpopular, and several former municipalities, totalling 13% of the population of the island, voted to leave the newly unified city in separate referendums in June 2004. The demerger took place on January 1, 2006, leaving 15 municipalities on the island, including Montreal.
[edit] Geography

Montreal is located in the southwest of the province of Quebec, approximately 275 kilometres (168 miles) southwest of Quebec City, the provincial capital, and 167 kilometres (104 mi) east of Ottawa, the federal capital. It also lies 502 kilometres (312 mi) northeast of Toronto, 407 kilometres (253 mi) northwest of Boston and 530 kilometres (329 mi) directly north of New York City.[34]
The city is located on the central and eastern portions of the Island of Montreal at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa Rivers. The port of Montreal lies at one end of the Saint Lawrence Seaway, which is the river gateway that stretches from the Great Lakes into the Atlantic Ocean.[35] Montreal is defined by its location in between the St. Lawrence river on its south, and by the Rivière des Prairies on its north. The city is named after the most prominent geographical feature on the island, a three-head hill called Mount Royal, topped at 232 m above sea level.[36]
Montreal is at the centre of the Montreal Metropolitan Community, and is bordered by the city of Laval to the north, Longueuil, St. Lambert, Brossard, and other municipalities to the south, Repentigny to the east and the West Island municipalities to the west. The anglophone enclaves of Westmount, Montreal West, Hampstead, Côte Saint-Luc, the Town of Mount Royal and the francophone enclave Montreal East are all entirely surrounded by the city of Montreal.[37]
[edit] Climate
Montreal lies at the confluence of several climatic regions. Usually, the climate is classified as humid continental or hemiboreal (Köppen climate classification Dfb).[38]
Precipitation is abundant with an average snowfall of 2.25 metres (84 in) per year in the winter. Regular rainfall throughout the year averages 900 mm (35.3 in). Summer is the wettest season statistically, but it is also the sunniest.[39]
The coldest month of the year is January which has a daily maximum temperature of −5.7 °C (22 °F) — averaging a daily low of −14.7 °C (6 °F).[40] Due to wind chill, the perceived temperature can be much lower than the actual temperature, and wind chill factor is often included in Montreal weather forecasts. The warmest month is July which has an average daily high of 26.2 °C (79 °F); lower nighttime temperatures make an average of 20.9 °C (70 °F) thus air exchangers often achieve the same result as air conditioners. The lowest temperature ever recorded was −37.8 °C (−36 °F) on January 15, 1957 and the highest temperature ever recorded was 37.6 °C (100 °F) on August 1, 1975.[40] High humidity is common in the summer which makes the perceived temperature higher than the actual temperature. In spring and autumn, rainfall averages between 55 millimetres (2 in) and 94 millimetres (4 in) a month. Some snow in spring and autumn is normal. Similarly, late heat waves as well as "Indian summers" are a regular feature of the climate.[41]
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.9 (57) |
15 (59) |
25.6 (78) |
30 (86) |
33.9 (93) |
35 (95) |
35.6 (96) |
37.6 (100) |
33.5 (92) |
28.3 (83) |
21.7 (71) |
18 (64) |
37.6 (100) |
| Average high °C (°F) | -5.7 (22) |
-3.9 (25) |
2.2 (36) |
10.7 (51) |
19.0 (66) |
23.6 (74) |
26.2 (79) |
24.8 (77) |
19.7 (67) |
12.7 (55) |
5.3 (42) |
-2.2 (28) |
11.1 (52) |
| Average low °C (°F) | -14.7 (6) |
-12.9 (9) |
-6.7 (20) |
0.6 (33) |
7.7 (46) |
12.7 (55) |
15.6 (60) |
14.3 (58) |
9.4 (49) |
3.4 (38) |
-2.1 (28) |
-10.4 (13) |
1.4 (35) |
| Record low °C (°F) | -37.8 (-36) |
-33.9 (-29) |
-29.4 (-21) |
-15 (5) |
-4.4 (24) |
0 (32) |
6.1 (43) |
3.3 (38) |
-2.2 (28) |
-7.2 (19) |
-19.4 (-3) |
-32.4 (-26) |
-37.8 (-36) |
| Precipitation mm (inches) | 78.3 (3.08) |
61.5 (2.42) |
73.6 (2.9) |
78.0 (3.07) |
76.3 (3) |
83.1 (3.27) |
91.3 (3.59) |
92.7 (3.65) |
92.6 (3.65) |
77.8 (3.06) |
92.6 (3.65) |
81.3 (3.2) |
978.9 (38.54) |
| Source: Environment Canada[40] 27 Jan 2009 | |||||||||||||
[edit] Cityscape
[edit] Architecture
For over a century and a half, Montreal was the industrial and financial centre of Canada.[42] The variety of buildings included factories, elevators, warehouses, mills, and refineries which today provide a legacy of historic and architectural interest, especially in the downtown area and the Old Port area.
Today there are also many historical buildings in Old Montreal still in their original form: Notre-Dame de Montréal Basilica, Bonsecours Market, and the impressive 19th-century headquarters of all major Canadian banks on St. James Street (French: Rue Saint Jacques). Saint Joseph's Oratory, completed in 1934, Ernest Cormier's Art Deco Université de Montréal main building, the landmark Place Ville Marie office tower, the controversial Olympic Stadium and surrounding structures, are but a few notable examples of 20th century architecture.
Pavilions designed for the 1967 International and Universal Exposition, popularly known as Expo 67, featured a wide range of architectural designs. Though most pavilions were temporary structures, several remaining structures have become Montreal landmarks, including the geodesic dome US Pavilion, now the Montreal Biosphere, as well as Moshe Safdie's striking Habitat 67 apartment complex.
The Montreal Metro is filled with a profusion of public artwork by some of the biggest names in Quebec culture. The design and ornamentation of each station in the Metro system is unique.
In 2006, the city was recognized by the international design community as a UNESCO City of Design, one of the three world design capitals.[43]
[edit] Neighbourhoods
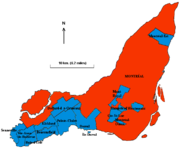
The city of Montreal is composed of 19 large boroughs which are further subdivided into smaller neighbourhoods.[44] The boroughs are Ahuntsic-Cartierville, Anjou, Côte-des-Neiges–Notre-Dame-de-Grâce,Lachine, LaSalle, Le Plateau-Mont-Royal, Le Sud-Ouest, L'Île-Bizard–Sainte-Geneviève, Mercier–Hochelaga-Maisonneuve, Montréal-Nord, Outremont, Pierrefonds-Roxboro, Rivière-des-Prairies–Pointe-aux-Trembles, Rosemont–La Petite-Patrie, Saint-Laurent, Saint Leonard, Verdun, Ville-Marie and Villeray–Saint-Michel–Parc-Extension.
The borough with the most neighbourhoods is Ville-Marie, which includes the city's downtown, the historical district of Old Montreal, Chinatown, the Gay Village, the Latin Quarter, the recently gentrified Quartier international and Cité Multimédia as well as the Quartier des Spectacles which is currently under development. Other neighbourhoods of interest in the borough include the affluent Golden Square Mile neighbourhood at the foot of Mount Royal and the Shaughnessy Village/Quartier Concordia area home to thousands of students at Concordia University. The borough also comprises most of Mount Royal Park, Saint Helen's Island, and Île Notre-Dame.
The Plateau Mont-Royal borough has historically been a working-class francophone area. The largest neighbourhood is the Plateau (not to be confused with the whole borough), which is currently undergoing considerable gentrification, and a 2001 study deemed it as Canada's most creative neighbourhood due to the fact that 8% of its labour force is composed of artists.[45] The neighbourhood of Mile End in the northwestern part of the borough, has historically been a very multicultural area of the city, and features two of Montreal's well-known bagel establishments, St-Viateur Bagel and Fairmount Bagel. The McGill Ghetto is located in the extreme southwestern portion of the borough, its name being derived from the fact that it is home to thousands of McGill University students.
The Sud-Ouest borough was home to much of the city's industry during the late 19th and early-to-mid 20th century. The borough includes the traditionally working-class Irish neighbourhoods of Griffintown, Goose Village and Pointe-Saint-Charles as well as the low-income neighbourhoods of Saint-Henri and Little Burgundy.
Other notable neighbourhoods in Montreal include the multicultural areas of Notre-Dame-de-Grâce and Côte-des-Neiges in the Côte-des-Neiges–Notre-Dame-de-Grâce borough, as well as Little Italy in the borough of Rosemont–La Petite-Patrie and Hochelaga-Maisonneuve, home of Montreal's Olympic Stadium in the borough of Mercier–Hochelaga-Maisonneuve.
[edit] Mount Royal
The mountain is the site of Mount Royal Park (French: Parc du Mont-Royal), one of Montreal's largest greenspaces. The park, most of which is wooded, was designed by Frederick Law Olmsted, who also designed New York's Central Park, and inaugurated in 1876.[46]
The park contains two belvederes, the more prominent of which is the Kondiaronk Belvedere, a semicircular plaza with a chalet, overlooking downtown Montreal. Other features of the park are Beaver Lake, a small man-made lake; a short ski slope; a sculpture garden; Smith House, an interpretive centre; and a well-known monument to Sir George-Étienne Cartier. The park hosts athletic, tourist, and cultural activities.
The mountain is also home to two major cemeteries, Notre-Dame-des-Neiges (founded in 1854) and Mount Royal (1852). Mount Royal Cemetery is a 165 acres (67 ha) terraced cemetery on the north slope of Mount Royal in the borough of Outremont. Cimetière Notre-Dame-des-Neiges is much larger, predominantly French-Canadian and officially Catholic.[47] More than 900,000 people are buried there.[48]
Mount Royal Cemetery contains more than 162,000 graves and is the final resting place for a number of notable Canadians. It includes a veterans section with several soldiers who were awarded the British Empire's highest military honour, the Victoria Cross. In 1901 the Mount Royal Cemetery Company established the first crematorium in Canada.[49]
The first cross on the mountain was placed there in 1643 by Paul Chomedey de Maisonneuve, the founder of the city, in fulfilment of a vow he made to the Virgin Mary when praying to her to stop a disastrous flood.[46] Today, the mountain is crowned by a 31.4 m-high (103 ft) illuminated cross, installed in 1924 by the Société Saint-Jean-Baptiste and now owned by the city.[46] It was converted to fibre-optic light in 1992.[46] The new system can turn the lights red, blue, or purple, the last of which is used as a sign of mourning between the death of the Pope and the election of the next.[50]


[edit] Demographics
| Population of Montreal, by year | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | City | Island | CMA |
| 1871 | 107,225 | — | 174,090[51] |
| 1881 | 140,747 | — | 223,512[51] |
| 1891 | 216,650 | — | 308,169[51] |
| 1901 | 267,730 | — | 393,665[51] |
| 1911 | 467,986 | — | 594,812[51] |
| 1921 | 618,506 | — | 774,330[51] |
| 1931 | 818,577[51] | 1,003,868[52] | 1,064,448[51] |
| 1941 | 903,077[51] | 1,116,800[52] | 1,192,235[51] |
| 1951 | 1,036,542[51] | 1,320,232[52] | 1,539,308[51] |
| 1961 | 1,257,537[51] | 1,747,696[53] | 2,215,627[51] |
| 1971 | 1,214,352[51] | 1,959,180[53] | 2,743,208[51] |
| 1981 | 1,018,609[51] | 1,760,122[53] | 2,862,286[51] |
| 1991 | 1,017,666[51] | 1,775,871[53] | 3,127,242[51] |
| 2001 | 1,812,723 | 1,812,723 | 3,426,350[51] |
| 2006 | 1,620,693 | 1,854,442 | 3,635,571[51] |
According to Statistics Canada, at the 2006 Canadian census the city of Montreal proper had 1,620,693 inhabitants.[1] However, 3,635,571 lived in the Montreal Census Metropolitan Area (CMA) at the same 2006 census, up from 3,451,027 at the 2001 census (within 2006 CMA boundaries), which means a population growth of +1.05% per year between 2001 and 2006.[3] In the 2006 census, children under 14 years of age (621,695) constituted 17.1 percent, while inhabitants over 65 years of age (495,685) numbered 13.6 percent of the total population.[1] People of European ethnicities formed the largest cluster of ethnic groups in Montreal, mostly of French, Irish, Italian, and British origins.[54] Some 26 percent of the population of Montreal and 16.5 percent of Greater Montreal are members of a visible minority (non-white) group.[55] Black Canadians contribute to the largest visible minority group in Greater Montreal, numbering some 169,065 or 7.2%, which is the second-largest community of African-origin people in Canada, after Toronto.[55] Other groups, such as Jews, Arabs, Hispanics, South Asians, and East Asians are also large in number.
According to a recently published report by the city of Montreal, the island is expected to number 1,991,200 by 2012, with 4,000,000+ in the Greater Montreal Area, an increase of 15.8% over 2001.[56]
Visible minorities are defined by the Canadian Employment Equity Act as "persons, other than Aboriginals, who are non-Caucasian in race or non-white in colour."[57]
| 1996[58] | 2001[59] | 2006[13] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| French | 71.2% | 72.1% | 70.5% |
| English | 19.4% | 18.5% | 18.5% |
| Other language | 13.4% | 13.1% | 14.6% |
| Note that percentages add up to more than 100% because some people speak two or more languages at home. |
|||
In terms of mother tongue language (first language learned), the 2006 census reported that in the Greater Montreal Area, 66.5% spoke French as a first language, followed by English at 13.2%, while 0.8% spoke both as a first language.[60] The remaining 22.5% of Montreal-area residents are allophones, speaking languages including Italian (3.5%), Arabic (3.1%), Spanish (2.6%), Creole (predominantly of Haitian origin) (1.4%), Chinese (1.2%), Greek (1.2%), Portuguese (0.9%), Romanian (0.7%), Vietnamese (0.7%), and Russian (0.5%).[60] In terms of additional languages spoken, a unique feature of Montreal throughout Canada, noted by Statistics Canada, is the working knowledge of both French and English by most of its residents.
The Greater Montreal Area is overwhelmingly Roman Catholic; however, church attendance in Quebec is among the lowest in Canada.[61] Historically Montreal has been a centre of Catholicism in North America with its numerous seminaries and churches, including the Notre-Dame Basilica, the Cathédrale Marie-Reine-du-Monde, and Saint Joseph's Oratory. Some 84.6 percent of the total population is Christian,[62] largely Roman Catholic (74.5%), which is largely due to French, Italian and Irish origins. Protestants which include Anglican, United Church, Lutheran and other denominations number 7.0%, with a further 3.0% consisting mostly of Orthodox Christians, fuelled by a large Greek population. Due to the large number of non-European cultures, there is a diversity of non-Christian religions. Islam is the largest non-Christian group, with some 100,185 members, the second-largest concentration of Muslims in Canada, constituting 3%.[62] The Jewish community in Montreal has a population of 88,765.[62] In cities such as Côte-Saint-Luc and Hampstead, Jewish people constitute the majority,[63][64] or a substantial part of the population. As recently as 1971 the Jewish community in Greater Montreal was as high as 109,480.[53] Political and economic uncertainties led many to leave Montreal and the province of Quebec.[65]
[edit] Economy
Montreal's economy is the second of all cities in Canada[66] and the first in Quebec.[67] The city is today an important centre of commerce, industry, technology, culture, finance, and world affairs.

Montreal industries include aerospace, electronic goods, pharmaceuticals, printed goods, software engineering, telecommunications, textile and apparel manufacturing, tobacco and transportation. The service sector is also strong and includes civil, mechanical and process engineering, finance, higher education, and research and development. In 2002, Montreal ranked as the 4th largest centre in North America in terms of aerospace jobs.[68]
The Port of Montreal is the largest inland port in the world handling 26 million tonnes of cargo annually.[69] As one of the most important ports in Canada, it remains a trans-shipment point for grain, sugar, petroleum products, machinery, and consumer goods. For this reason, Montreal is the railway hub of Canada and has always been an extremely important rail city; it is home to the headquarters of the Canadian National Railway,[70] and was home to the headquarters of the Canadian Pacific Railway until 1995.[71]
The headquarters of the Canadian Space Agency are located in Longueuil, southeast of Montreal.[72] Montreal also hosts the headquarters of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO, a United Nations body);[73] the World Anti-Doping Agency (an Olympic body);[74] the International Air Transport Association (IATA);[75] and the International Gay and Lesbian Chamber of Commerce (IGLCC),[76] as well as some 60 other international organizations in various fields.
In 2006 Montreal was named a UNESCO City of Design, only one of three design capitals of the world (with the others being Berlin and Buenos Aires).[77] This distinguished title recognizes Montreal's design community. Since 2005 the city has also been home for the International Council of Graphic Design Associations (Icograda);[78] the International Design Alliance (IDA).[79]
Montreal is also a centre of film and television production. The headquarters of Alliance Films and five studios of the Academy Award-winning documentary producer National Film Board of Canada can be found here, as well as the head offices of Telefilm Canada, the national feature-length film and television funding agency. Given its eclectic architecture and broad availability of film services and crew members, Montreal is a popular filming location for feature-length films, and sometimes stands in for European locations.[80][81] The city is also home to many recognized cultural, film and music festivals (Just For Laughs, Montreal Jazz Festival, and others), which contribute significantly to its economy. It is also home to one of the world's largest cultural enterprises, the Cirque du Soleil.[82]
The video game industry is also booming in Montreal since 1997, coinciding with the opening of Ubisoft Montreal.[83] Recently, the city has attracted world leading game developers and publishers studios such as Ubisoft, EA, Eidos Interactive, Artificial Mind and Movement, Strategy First, mainly because video games jobs have been heavily subsidized by the provincial government.
A diverse range of companies are headquartered in Greater Montreal including Rio Tinto Alcan, Desjardins Group, Bombardier, Canadian National Railway, CGI Group, Air Canada, Air Transat, CAE, Saputo, Cirque du Soleil, Quebecor, Power Corporation, Bell Canada, SNC-Lavalin, Hydro-Québec, AbitibiBowater, Laurentian Bank, Pratt and Whitney Canada, Molson, Tembec, Alimentation Couche-Tard, MEGA Brands, National Bank of Canada, VIA Rail and the Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec.
Greater Montreal had a GDP of $120 billion in 2005, placing it 39th in the world.[84] It is expected to grow to almost $126 billion in 2008 and $140 billion by 2012.[85]
[edit] Culture
Montreal was referred to as "Canada's Cultural Capital" by Monocle Magazine.[86] The city is Canada's centre for French language television productions, radio, theatre, film, multimedia and print publishing. Montreal's many cultural communities have given it a distinct local culture.
As a North American city, Montreal shares many cultural characteristics with the rest of the continent. It has a tradition of producing both jazz and rock music. The city has also produced much talent in the fields of visual arts, theatre, music, and dance. Yet, being at the confluence of the French and the English traditions, Montreal has developed a unique and distinguished cultural face. Another distinctive characteristic of Montreal culture life is to be found in the animation of its downtown, particularly during summer, prompted by cultural and social events, particularly festivals. The city's largest festival is the Just for Laughs comedy festival, which is the largest in the world of its kind. Other popular festivals include the Montreal International Jazz Festival, the Francofolies and the Montreal Fireworks Festival.
A cultural heart of classical art and the venue for many summer festivals, the Place des Arts is a complex of different concert and theatre halls surrounding a large square in the eastern portion of downtown. Place des Arts harbours the headquarters of one of the world's foremost orchestras, the Montreal Symphony Orchestra. The Orchestre Métropolitain du Grand Montréal and the chamber orchestra I Musici de Montréal are two other well-regarded Montreal orchestras. Also performing at Place des Arts is the Opéra de Montréal and the city’s chief ballet company Les Grands Ballets Canadiens. Internationally recognized avant-garde dance troupes such as La La La Human Steps, O Vertigo, and the Fondation Jean-Pierre Perreault have toured the world and worked with international popular artists on videos and concerts. The unique choreography of these troupes has paved the way for the success of the world-renowned Cirque du Soleil.

Nicknamed la ville aux cent clochers ("the city of a hundred belltowers"), Montreal is renowned for its churches. Indeed, as Mark Twain once noted, "This is the first time I was ever in a city where you couldn't throw a brick without breaking a church window."[87] The city has four Roman Catholic basilicas: Mary, Queen of the World Cathedral, the aforementioned Notre-Dame Basilica, St. Patrick's Basilica, and Saint Joseph's Oratory. The Oratory is the largest church in Canada, with the second largest copper dome in the world after that of Saint Peter's Basilica in Rome.[88]
[edit] Sports

The most popular sport in Montreal is Ice hockey. The city's professional hockey team, the Montreal Canadiens, are one of the Original Six NHL teams, and boast an NHL-record 24 Stanley Cup championships. The New York Yankees are the only other team in North American sports to have more championship titles with 26.
Montreal has a storied baseball history. The city was the home of the Montreal Royals until 1960 and Jackie Robinson broke the baseball colour barrier with the Royals in 1946 in an emotionally difficult year where Robinson was forever grateful for the local fans' fervent support[89] Major League Baseball came to town in the form of the Montreal Expos in 1969. They played their games at Jarry Park until moving into Olympic Stadium in 1977. After 37 years in Montreal, the team relocated to Washington, DC in 2005 and re-branded themselves as the Washington Nationals.[90]
The Montreal Alouettes of the CFL draw packed crowds at the small but picturesque Molson Stadium for their regular season games. Late season and playoff games are played at the much larger, enclosed Olympic Stadium, which will also play host to the 2008 Grey Cup. The McGill Redmen, Concordia Stingers, and Université de Montréal Carabins play in the CIS university football league.
The city's USL First Division soccer team is called the Montreal Impact. They play at a soccer-specific stadium called Saputo Stadium. The Montreal games of the FIFA 2007 FIFA U-20 World Cup were held at Olympic Stadium.[91]
Montreal was formerly the site of a high-profile racing event each year: the Canadian Grand Prix of F1 racing, and during a one time event, a NASCAR race in the Nationwide Series. These races took place on the famous Circuit Gilles Villeneuve on Île Notre-Dame, where the Champ Car series also raced from 2002 until 2007.. In 2008, after 29 years on the same circuit, the F1 Grand Prix left Montreal, with the event moved to other cities (the 2009 calendar has Abu Dhabi scheduled).

Uniprix Stadium was built in 1993 and is used for the annual Rogers Cup Tennis Masters tournament. The ATP men's tennis tour and the Sony Ericsson WTA women's tennis tour switch between Montreal and Toronto every year.[92]
Montreal was the host of the 1976 Summer Olympic Games. The stadium alone cost $1.5 billion,[93], with interest that figure ballooned to nearly $3 billion, and was only paid off in December 2006.[94] Montreal hosted the first ever World Outgames in the summer of 2006, attracting over 16,000 participants engaged in 35 sporting activities.
Five beaches around the island, in addition to a network of parks that include one on the Mont Royal, offer a set of recreational activities enjoyed by the local population.
| Club | League | Sport | Venue | Established | Championships |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montreal Canadiens | NHL | Ice hockey | Bell Centre | 1909 | 24 |
| Montreal Alouettes | CFL | Football | Percival Molson Memorial Stadium Olympic Stadium |
1946–87 1996–today |
7 |
| Montreal Impact | USL | Soccer | Saputo Stadium | 1993 | 2 |
| Montreal Junior Hockey Club | QMJHL | Ice hockey | Verdun Auditorium | 2008 | 0 |
| Montreal Sasquatch | PBL | Basketball | Centre Pierre Charbonneau | 2008 | 0 |
| Quebec Caribou | RCSL | Rugby union | Dollard-des-Ormeaux | 1998 | 0 |
[edit] Media
Montreal is well served by a variety of media, including several English and French language television stations, newspapers, radio stations, and magazines. There are four over-the-air English-language television stations: CBC Television, CTV, Global and E! which also airs multicultural programming. There are also five over-the-air French-language television stations: Radio-Canada, TVA, TQS, Télé-Québec, and Canal Savoir.
Montreal has four daily newspapers. The English-language Montreal Gazette and the French-language La Presse, Le Journal de Montréal and Le Devoir. There are also two free French dailies, Métro and 24 Heures. Montreal also has myriad weekly tabloids and community newspapers serving various neighbourhoods, ethnic groups and schools.
There are 11 AM and 23 FM radio stations in Montreal. Of these 14 stations broadcast in English, 17 broadcast in French, 3 broadcast in multiple languages and one station is bilingual.
[edit] Government
The head of the city government in Montreal is the mayor, who is first among equals in the City Council. The mayor is Gérald Tremblay, who is a member of the Union des citoyens et des citoyennes de l'Île de Montréal (English: Montreal Island Citizens Union). The city council is a democratically elected institution and is the final decision-making authority in the city, although much power is centralized in the executive committee. The Council consists of 73 members from all boroughs of the city.[95] The Council has jurisdiction over many matters, including public security, agreements with other governments, subsidy programs, the environment, urban planning, and a three-year capital expenditure program. The City Council is also required to supervise, standardize or approve certain decisions made by the borough councils.
Reporting directly to the City Council, the executive committee exercises decision-making powers similar to that of the cabinet in a parliamentary system and is responsible for preparing various documents including budgets and by-laws, submitted to the City Council for approval. The decision-making powers of the executive committee cover, in particular, the awarding of contracts or grants, the management of human and financial resources, supplies and buildings. It may also be assigned further powers by the City Council.
Standing committees are the council's prime instruments for public consultation. They are responsible for the public study of pending matters and for making the appropriate recommendations to the council. They also review the annual budget forecasts for departments under their jurisdiction. A public notice of meeting is published in both French and English daily newspapers at least seven days before each meeting. All meetings include a public question period. The standing committees, of which there are seven, have terms lasting two years. In addition, the City Council may decide to create special committees at any time. Each standing committee is made up of seven to nine members, including a chairman and a vice-chairman. The members are all elected municipal officers, with the exception of a representative of the government of Quebec on the public security committee.
The city of Montreal is only one component of the larger Communauté Métropolitaine de Montréal (English: Montreal Metropolitan Community or MMC), which is in charge of planning, coordinating, and financing economic development, public transportation, garbage collection and waste management, etc., across the metropolitan area of Montreal. The president of the CMM is the mayor of Montreal. The CMM covers 4,360 square kilometres (1,683 sq mi), with 3.6 million inhabitants in 2006.[96]
[edit] Education


With access to six universities and twelve junior colleges in an 8 kilometre (5 mi) radius, Montreal has the highest concentration of post-secondary students of all major cities in North America (4.38 students per 100 residents, followed by Boston at 4.37 students per 100 residents).[97]
There are two francophone universities located in the city of Montreal:
- Université de Montréal (UdeM) is the second largest research university in Canada. Two separate institutions are affiliated to the university: the École Polytechnique de Montréal (School of Engineering) and HEC Montréal (School of Business).
- Université du Québec à Montréal (UQÀM) is the Montreal campus of Université du Québec. UQÀM generally specializes in liberal-arts. It has several separately run schools, notably the École de technologie supérieure (ETS), the École nationale d'administration publique (ENAP) and the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS).
Additionally, two French-language universities, Université de Sherbrooke and Université Laval have campuses in the nearby suburb of Longueuil on Montreal's south shore.
There are also two anglophone universities in the city:
- McGill University is one of the oldest and most renowned schools in Canada, a major research university, and has been rated as Canada's best university by various sources,[98] and the twelfth best in the world by Quacquarelli Symonds.[99]
- Concordia University is the other English-language university, created from the merger of Sir George Williams University and Loyola College.[100] According to a worldwide ranking by the École des Mines de Paris, Concordia ranks first among Canadian and 33rd among world universities in terms of graduates occupying the rank of Chief Executive Officer at Fortune 500 companies.[101]
The education system in the province of Quebec is slightly different from other systems in North America. Between the high school and university levels, there is an additional college level called CEGEP. It is at the same time a preparatory school (preparing students for admission to university) and a technical school (offering courses which lead to technical diplomas and specializations). In Montreal, seventeen CEGEPs offer courses in French and five in English.
English-language elementary and secondary public schools on Montreal Island are operated by the English Montreal School Board[102] and the Lester B. Pearson School Board.[103] French-language elementary and secondary public schools in Montreal are operated by the Commission scolaire de Montréal (CSDM),[104] Commission scolaire Marguerite-Bourgeoys (CSMB)[105] and the Commission scolaire Pointe-de-l'Île (CSPI).[106]
[edit] Transportation
Like many major cities, Montreal has a problem with vehicular traffic congestion, especially from off-island suburbs such as Laval on Île Jésus, and Longueuil on the south shore. The width of the Saint Lawrence River has made the construction of fixed links to the south shore expensive and difficult. There are only four road bridges along with one road tunnel, two railway bridges, and a metro line. The far narrower Rivière des Prairies, separating Montreal from Laval, is spanned by eight road bridges (six to Laval and two directly to the north shore).
The island of Montreal is a hub for the Québec Autoroute system, and is served by Québec Autoroutes A-10 (known as the Bonaventure Expressway on the island of Montreal), A-15 (aka the Decarie Expressway south of the A-40 and the Laurentian Autoroute to the north of it), A-13 (aka Autoroute Chomedey), A-20, A-25, A-40 (part of the Trans-Canada Highway system, and known as "The Metropolitan" or simply "The Met" in its elevated mid-town section), A-520, and A-720 (aka the Ville-Marie Autoroute). Many of these Autoroutes are frequently congested at rush hour.[107] However, in recent years, the government has acknowledged this problem and is working on long-term solutions to alleviate the congestion. One such example is the extension of Quebec Autoroute 30 on Montreal's south shore, which will serve as a bypass.[108]
Public local transport is served by a network of buses, subways, and commuter trains that extend across and off the island. The subway and bus system is operated by the Société de transport de Montréal (STM). The STM bus network consists of 165 daytime and 20 night-time service routes, and provides adapted transport and limited wheelchair-accessible buses.[109]
Montreal's Metro was inaugurated in 1966 and today has 68 stations spread out along its four lines.[110] Each station was designed by different architects with individual themes and features original artwork, and the trains themselves run on rubber tires, making the system quieter than most.[111] The project was initiated by Montreal Mayor Jean Drapeau, who would later bring the Summer Olympic Games to Montreal in 1976. The metro system has long had a station on the South Shore in Longueuil, and has only recently been extended to the city of Laval, north of Montreal with 3 new stations.[112]
The commuter rail system is managed and operated by the Agence métropolitaine de transport, and reaches the outlying areas of Greater Montreal. Montreal's commuter rail network had 15.7 million passengers in 2007, making it the sixth busiest in North America following New York City, Chicago, Boston, Philadelphia, and Toronto.[113]
[edit] Air
Montreal has two international airports, one for passenger flights only, and the other for cargo. Montréal-Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport (also known as Dorval Airport) in the City of Dorval serves all commercial passenger traffic and is the headquarters for Air Canada[114] and Air Transat.[115] To the north of the city is Montréal-Mirabel International Airport in Mirabel, which was envisioned as Montreal's primary airport but which now serves cargo flights along with MEDEVACs and general aviation as well as some passenger services.[116][117][118][119][120] In 2008, Montreal-Trudeau was the fourth busiest airport in Canada by both passenger traffic and aircraft movements, behind Toronto Pearson, Vancouver and Calgary. In 2008 the airport handled 12,379,843 passengers,[121] and 225,219 aircraft movements.[122] With 59.7% of its passengers being on non-domestic flights it has the largest percentage of international flights of any Canadian airport.[121] Trudeau airport is served by 40 carriers to over 100 destinations worldwide.[123] Airlines servicing Trudeau offer flights to Africa, Central America, the Caribbean, Europe, the United States, Mexico and other destinations within Canada. It is the only Canadian airport that offers non-stop service to Africa and it also contains the largest duty free shop in North America.[124]
[edit] Rail

Montreal-based VIA Rail, provides rail service to other cities in Canada, particularly to Quebec City and Toronto with several Quebec City-Windsor Corridor. Amtrak, the U.S. national passenger rail system, also provides service to Montreal, operating its Adirondack daily between Montreal and New York City. All intercity trains and most commuter trains operate out of Central Station. The rest of the commuter trains operate out of the Lucien-L'Allier Station or at Parc metro station. Some of the trains ending their route at Parc metro station have an express bus that links downtown Montreal to the station.
Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), which is now headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, was founded here in 1881.[125] Its corporate headquarters occupied Windsor Station at 910 Peel Street until 1995.[71] With the Port of Montreal kept open year round by icebreakers, lines to Eastern Canada became surplus, and now Montreal is the railway's eastern and intermodal freight terminus.[126] CPR connects at Montreal with the Port of Montreal, the Delaware & Hudson Railway to New York, the Quebec-Gatineau Railway to Quebec City and Buckingham, the Montreal, Maine & Atlantic to Halifax, and CN Rail. The CPR's flagship train, The Canadian, once ran daily from Windsor Station to Vancouver, all passenger services have since been transferred to VIA Rail Canada.
Montreal-based Canadian National Railways (CN) was formed during in 1919 by the Canadian Government following a series of country-wide rail bankruptcies. CN was formed from the lines of the Grand Trunk, Midland and Canadian Northern Railways, and has risen to become CPR's chief rival in freight carriage in Canada.[127] Like the CPR, CN has divested itself of passenger services in favour of VIA Rail Canada.[128]
[edit] Sister cities
Montreal has eight sister cities:
 Yerevan (Armenia) – 1998[129]
Yerevan (Armenia) – 1998[129] Shanghai (China) – 1985[130]
Shanghai (China) – 1985[130] Lyon, Rhône-Alpes (France) – 1979[131]
Lyon, Rhône-Alpes (France) – 1979[131] Paris, Île-de-France (France) – 2006[132]
Paris, Île-de-France (France) – 2006[132] Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh (India) – 2000[133]
Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh (India) – 2000[133] Hiroshima (Japan) – 1998[134]
Hiroshima (Japan) – 1998[134] Manila (Philippines) – 2005[135]
Manila (Philippines) – 2005[135] Busan (South Korea) – 2000[136]
Busan (South Korea) – 2000[136]
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ a b c d e "Population and dwelling counts, for Canada, provinces and territories, and census subdivisions (municipalities), 2006 and 2001 censuses - 100% data". Statistics Canada, 2006 Census of Population. 2007-03-13. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/popdwell/Table.cfm?T=302&SR=1&S=3&O=D&RPP=25&PR=24. Retrieved on 2007-03-13.
- ^ a b "Population and dwelling counts, for urban areas, 2006 and 2001 censuses - 100% data". Statistics Canada, 2006 Census of Population. 2007-03-13. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/popdwell/Table.cfm?T=801&PR=0&SR=1&S=3&O=D. Retrieved on 2007-03-13.
- ^ a b c "Population and dwelling counts, for census metropolitan areas and census agglomerations, 2006 and 2001 censuses - 100% data". Statistics Canada, 2006 Census of Population. 2007-03-13. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/popdwell/Table.cfm?T=201&S=3&O=D&RPP=150. Retrieved on 2007-03-13.
- ^ It is most common to omit the acute accent in English-language usage (Montreal), unless one is using a proper name where the context requires the use of the accent (e.g. Le Journal de Montréal, as compared to the Montreal Gazette), and to keep the accent in French-language usage (Montréal). This is also the approach favoured by The Canadian Press Style Book (ISBN 0-920009-32-8, at p. 234) and The Globe and Mail Style Book (ISBN 0-7710-5685-0, at p. 249). According to The Canadian Style (ISBN 1-55002-276-8, at pp. 263–4), the official style guide of the Government of Canada, the name of the city is to be written with an accent in all government materials.
- ^ "A Short History of Toronto". City of Toronto. http://www.toronto.ca/culture/history/history-shortversion.htm. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Old Montréal / Centuries of History". 2000-04. http://www.vieux.montreal.qc.ca/histoire/eng/v_mara.htm. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Island of Montreal" (in English). Natural Resoruces Canada. http://geonames.nrcan.gc.ca/education/montreal_e.php. Retrieved on 07-02-2008.
- ^ Poirier, Jean (1979), "Commission de toponymie du Québec", Island of Montréal, 5, Quebec: Canoma, pp. 6–8
- ^ "real". Merriam-Webster's Dictionary of Law. 2007-10-10. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/real. Retrieved on 2009-03-23.
- ^ Chapter 1, article 1, "Chartre de la Ville de Montréal" (in French). 2008. http://www2.publicationsduquebec.gouv.qc.ca/dynamicSearch/telecharge.php?type=2&file=/C_11_4/C11_4.htm. Retrieved on 2008-02-07.
- ^ Chapter 1, article 1, "Charter of Ville de Montréal" (in Ensligh). 2008. http://www.canlii.org/qc/laws/sta/c-11.4/20080115/whole.html. Retrieved on 2008-02-07.
- ^ Participatory Democracy: Prospects for Democratizing Democracy, Dimitrios I. Roussopoulos, C. George Benello, p.292. "It [Montreal] is second only to Paris as the largest primarily French-speaking city in the world."
- ^ a b "Population by language spoken most often at home and age groups, 2006 counts, for Canada and census metropolitan areas and census agglomerations – 20% sample data". http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/highlights/language/Table402.cfm?Lang=E&T=402&GH=8&SC=1&S=0&O=A. Retrieved on 2007-12-05.
- ^ "Place Royale and the Amerindian presence". Société de développement de Montréal. September 2001. http://www.vieux.montreal.qc.ca/tour/etape9/eng/9text3a.htm. Retrieved on 2007-03-09.
- ^ a b c Tremblay, Roland (2006). The Saint Lawrence Iroquoians. Corn People.. Montréal, Qc: Les Éditions de l'Homme.
- ^ "Jacques Cartier: New Land for the French King". Pathfinders & Passageways. http://www.collectionscanada.ca/2/24/h24-1330-e.html. Retrieved on 2007-02-26.[dead link]
- ^ Marsan, Jean-Claude (1990). Montreal in evolution. An historical analysis of the development of Montreal's architecture.. Montréal, Qc: Les Éditions de l'Homme.
- ^ a b Miquelon, Dale. "Ville-Marie (Colony)". The Canadian Encyclopedia. http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/index.cfm?PgNm=TCE&Params=A1ARTA0008371. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "Articles of the Capitulation of Montréal, 1760". MSN Encarta. 1760. http://ca.encarta.msn.com/sidebar_461511335/articles_of_the_capitulation_of_montreal_1760.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "Montreal :: Government". Student's Enclyclopedia. Encyclopaedia Britannica. http://student.britannica.com/comptons/article-204877/Montreal. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "Lachine Canal National Historic Site of Canada" (PDF). Parks Canada. 3. http://www.pc.gc.ca/lhn-nhs/qc/lachine/images/edu01c_E.pdf. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "Visiting Montréal, Canada". International Conference on Aquatic Invasive Species. http://www.icais.org/html/location.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "UNA-Canada: A Sense of Belonging". United Nations Association in Canada. http://www.unac.org/sb/en/hostcommunities/montreal.asp. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "Walking Tour of Old Montreal". Vehicule Press. http://www.vehiculepress.com/montreal/oldmontreal.html. Retrieved on 2008-01-30.
- ^ Arnold, Kathy (2008-06-03). "Montreal: a thrilling collision of cultures". The Daily Telegraph. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/destinations/northamerica/canada/762859/Montreal-a-thrilling-collision-of-cultures.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "DEPRESSION AND WAR 1930-1945". Montreal Archives Portal. City of Montreal. http://www2.ville.montreal.qc.ca/archives/500ans/portail_archives_en/rep_chapitre10/chapitre10-1.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ a b "Conscription for Wartime Service". Mount Allison University. 2001. http://www.mta.ca/about_canada/study_guide/debates/conscription.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "Camillien Houde". City of Montreal. http://www2.ville.montreal.qc.ca/archives/democratie/democratie_en/expo/maires/houde/index.shtm. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "THE EMERGENCE OF A MODERN CITY 1945-1960". Montreal Archives Portal. City of Montreal. http://www2.ville.montreal.qc.ca/archives/500ans/portail_archives_en/rep_chapitre11/chapitre11-1.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ Veltman, Calvin (1996). "Post-imperial English". Mouton de Gruyter. 206. http://books.google.ca/books?id=SIu244rlVu8C&pg=PA206&lpg=PA206&dq=montreal+decline+opening+seaway&source=bl&ots=FTZ8ymB7mQ&sig=TKsNKbQti3h8McRxayAJN6pWflI&hl=en&ei=v_TPSemxCJ_aswPYk7WhAw&sa=X&oi=book_result&resnum=6&ct=result#PPA206,M1. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "A new francophone conquest". Montreal Archives Portal. City of Montreal. http://www2.ville.montreal.qc.ca/archives/500ans/portail_archives_en/rep_chapitre12/chapitre12-3.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ Bowen, Arabella; John Shandy Watson (2001-2004). "The Ongoing Threat of Separatism". The Rough Guide to Montreal. Rough Guides. 272. http://books.google.ca/books?id=bprM-IjxCNIC&pg=PA272&lpg=PA272&dq=separatism+montreal+toronto+101+l%C3%A9vesque+exodus&source=bl&ots=aDLLd_CteY&sig=54u2VtfBVLZXqtFn6WVzmREqUQY&hl=en&ei=sfrPSZe5Eoq-MsjqiUw&sa=X&oi=book_result&resnum=1&ct=result. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "Montreal 1976". Olympic Games. International Olympic Committee. http://www.olympic.org/uk/games/past/index_uk.asp?OLGT=1&OLGY=1976. Retrieved on 2009-03-29.
- ^ "Cities located close to Montreal". Distance Calculator. Time and Date AS. 1995-2008. http://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/distances.html?n=165. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ "The St. Lawrence River". Great Canadian Rivers. 2007. http://www.greatcanadianrivers.com/rivers/stlawer/stlawer-home.html. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ "Island of Montreal". Geographical Names of Canada. Natural Resources Canada. 2007-09-17. http://geonames.nrcan.gc.ca/education/montreal_e.php. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ "Découpage du territoire montréalais en 2006" (in French) (PDF). Montréal en statistiques. Ville de Montréal. 2006. http://ville.montreal.qc.ca/pls/portal/docs/page/MTL_STATISTIQUES_FR/media/documents/Decoupage_territoire_montrealais_2006.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ "Canadian Climate Normals 1971-2000" (in English). http://www.climate.weatheroffice.ec.gc.ca/climate_normals/results_e.html?Province=ALL&StationName=montreal&SearchType=BeginsWith&LocateBy=Province&Proximity=25&ProximityFrom=City&StationNumber=&IDType=MSC&CityName=&ParkName=&LatitudeDegrees=&LatitudeMinutes=&LongitudeDegrees=&LongitudeMinutes=&NormalsClass=A&SelNormals=&StnId=5415&. Retrieved on 2006-12-18.
- ^ "WEATHER IN MONTREAL, CANADA". TopSightSeeing.com. http://www.topsightseeing.com/canada/montreal/weather/index.htm. Retrieved on 2009-02-26.
- ^ a b c "Canadian Climate Normals 1971-2000" (in English). http://www.climate.weatheroffice.ec.gc.ca/climate_normals/results_e.html?Province=ALL&StationName=montreal&SearchType=BeginsWith&LocateBy=Province&Proximity=25&ProximityFrom=City&StationNumber=&IDType=MSC&CityName=&ParkName=&LatitudeDegrees=&LatitudeMinutes=&LongitudeDegrees=&LongitudeMinutes=&NormalsClass=A&SelNormals=&StnId=5415&. Retrieved on 2006-12-18.
- ^ "Average Weather for Montreal, QC — Temperature and Precipitation". Weather.com. http://www.weather.com/outlook/travel/climatology/monthly/CAXX0301.
- ^ "Welcome to Industrial Montreal". McGill University. http://digital.library.mcgill.ca/industrial/intro.html. Retrieved on 2009-02-26.
- ^ "Cities appointed to the Creative Cities Network". UNESCO. http://portal0.unesco.org/culture/admin/ev.php?URL_ID=27810&URL_DO=DO_TOPIC. Retrieved on 2007-11-22.
- ^ "Neighbourhoods". Gromco, Inc.. Montreal Bits. 2005-2009. http://www.montrealbits.com/neighbourhoods.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-25.
- ^ "Artists by neighbourhood in Canada" (PDF). Canada 2001 Census. Hill Strategies. October 2005. 3. http://www.hillstrategies.com/docs/Artists_by_neighbourhood.pdf. Retrieved on 2009-03-25.
- ^ a b c d Berryman, Tom. "Short History of Mount Royal". Les amis de la montagne. http://www.lemontroyal.qc.ca/en/learn-about-mount-royal/short-history-of-mount-royal.sn. Retrieved on 2009-02-26.
- ^ Notre-Dame-des-Neiges Cemetery Mission[dead link]
- ^ "The cemeteries of Mount Royal". Les amis de la montagne. http://www.lemontroyal.qc.ca/carte/en/html//The-cemeteries-of-Mount-Royal-38.html. Retrieved on 2009-02-26.
- ^ "Mount Royal Crematorium". Mount Royal Cemetery. 2003. http://www.mountroyalcem.com/aboutus/locations/mr_crematorium.aspx?lang=en-CA. Retrieved on 2009-02-26.
- ^ Silverman, Craig (2004-06-14). "The future of the Mount Royal cross". Hour (magazine). http://www.hour.ca/news/brief.aspx?iIDArticle=3438. Retrieved on 2009-02-26.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v "Montréal En Bref". City of Montreal. http://ville.montreal.qc.ca/pls/portal/docs/PAGE/MTL_STATISTIQUES_FR/MEDIA/DOCUMENTS/MONTR%C9AL%20EN%20BREF_JUIN2007.PDF. Retrieved on 2007-06.
- ^ a b c "Vol. 1 - Table 2" (XLS). 1951 Canadian Census. University of Toronto. http://prod.library.utoronto.ca:8090/datalib/data/cc51/1951%20census%20-%20table%202_area%20and%20density%20of%20population.xls. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ a b c d e "Statistical Tables — Religion" (in English). Statistics Canada Census. Gouvernement du Québec. http://www.mels.gouv.qc.ca/REFORME/religion/html-ang/ang/text/app6.htm. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ "Ethnocultural Portrait of Canada, Highlight Tables, 2006 Census: Montreal (CMA)". Statistics Canada. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/highlights/ethnic/pages/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo=CMA&Code=462__&Data=Count&Table=2&StartRec=1&Sort=3&Display=All&CSDFilter=5000. Retrieved on 2008-04-02.
- ^ a b "Visible minority groups, 2006 counts, for Canada and census metropolitan areas and census agglomerations - 20% sample data". Canada 2006 Census. Statistics Canada. 04-02-2008. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/highlights/ethnic/pages/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo=CMA&Code=01&Table=1&Data=Count&StartRec=1&Sort=11&Display=Page&CSDFilter=5000. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ http://ville.montreal.qc.ca/pls/portal/docs/PAGE/TRANSPORT_V2_FR/MEDIA/DOCUMENTS/PLAN_DE_TRANSPORT2008.pdf
- ^ Visible Minority Population and Population Group Reference Guide, 2006 Census
- ^ (French) Institut de la statistique du Québec. "Tableau 2 - Langue maternelle et langues parlées à la maison, connaissance des langues officielles, 1996, 1991 et 1986 - Régions métropolitaines de recensement" (PDF). http://www.stat.gouv.qc.ca/publications/regional/pdf3/regRMR_3-4.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-03-16.
- ^ "Language Spoken Most Often at Home (8), Language Spoken at Home on a Regular Basis (9), Sex (3) and Age Groups (15) for Population, for Canada, Provinces, Territories, Census Metropolitan Areas 1 and Census Agglomerations, 2001 Census - 20% Sample Data". Statistics Canada, 2001 Census of Population. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census01/products/standard/themes/RetrieveProductTable.cfm?Temporal=2001&PID=55535&APATH=3&METH=1&PTYPE=55440&THEME=41&FOCUS=0&AID=0&PLACENAME=0&PROVINCE=0&SEARCH=0&GC=0&GK=0&VID=0&VNAMEE=&VNAMEF=&FL=0&RL=0&FREE=0&GID=431565. Retrieved on 2007-03-16.
- ^ a b "Montreal (CMA) - Detailed Mother Tongue". Canada 2006 Census. Statistics Canada. April 1, 2008. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/topics/RetrieveProductTable.cfm?ALEVEL=3&APATH=3&CATNO=97-555-XCB2006007&DETAIL=0&DIM=&DS=99&FL=0&FREE=0&GAL=0&GC=99&GK=NA&GRP=1&IPS=97-555-XCB2006007&METH=0&ORDER=1&PID=89186&PTYPE=88971&RL=0&S=1&ShowAll=No&StartRow=1&SUB=701&Temporal=2006&Theme=70&VID=0&VNAMEE=&VNAMEF=&GID=837977. Retrieved on 2008-05-18.
- ^ CBC Article - Church attendance declining in Canada
- ^ a b c "2001 Community Highlights for Montréal". Statistics Canada. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/Profil01/CP01/Details/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CMA&Code1=462__&Geo2=PR&Code2=24&Data=Count&SearchText=montreal&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&Custom=. Retrieved on 2007-08-02.
- ^ "2001 Community Highlights for Hampstead". Statistics Canada. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/profil01/CP01/Details/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2466060&Geo2=PR&Code2=24&Data=Count&SearchText=montreal&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All. Retrieved on 2007-08-02.
- ^ "2001 Community Highlights for Côte-Saint-Luc". Statistics Canada. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/Profil01/CP01/Details/Page_Custom.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=2466055&Geo2=PR&Code2=24&Data=Count&SearchText=C%F4te-Saint-Luc&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=24&B1=Custom. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ "The Jewish Communities of Canada" (in English). Am Yisrael. http://www.amyisrael.co.il/na/canada/. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ Metropolitan Toronto 1st with $209 Billion US in 2005, Metropolitan Montreal 2nd with $120 Billion US also in 2005. [1]
- ^ In 2007, Metropolitan Montreal was responsible for $123 Billion of Quebec's $249 Billion USD GDP
- ^ (PDF)AEROSPACE: Metro Montreal 2003, Strategic Profile. Montreal, Quebec: thomas finney. 1760. http://www.montrealinternational.com/docs/profil/Aero_En_2003.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-01-03.
- ^ "The Port of Montreal unveils its project, which will generate $3.4 billion in annual economic spinoffs for Montreal" (PDF). Press Release. Port of Montreal. April 17, 2008. http://www.port-montreal.com/news/en_77_2.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ "Contact Us — CN Mailing Addresses". Canadian National Railway. http://www.cn.ca/contactus/en_HomeContactsUsCNMailingAddresses.shtml. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.[dead link]
- ^ a b Nemeth, Mary; Liz Warwick (December 4, 1995). "CP Rail Leaves Montreal". The Canadian Encyclopedia. http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/index.cfm?PgNm=TCE&Params=M1ARTM0010525. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ "CSA Headquarters". Contact Us. Canadian Space Agency. http://www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/contact.asp. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ "ICAO Premises". International Civil Aviation Organization. http://www.icao.int/icao/en/premises.htm. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ "Regional Offices". World Anti-Doping Agency. http://www.wada-ama.org/en/dynamic.ch2?pageCategory.id=261. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ "Our Offices". About Us. International Air Transport Association. http://www.iata.org/about/offices. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ "Contact Us". International Gay and Lesbian Chamber of Commerce. http://www.iglcc.org/en/contact.php. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ "Montreal, Canada appointed a UNESCO City of Design". UNESCO. 2006-06-07. http://portal.unesco.org/culture/en/ev.php-URL_ID=30945&URL_DO=DO_TOPIC&URL_SECTION=201.html.
- ^ "CONTACT". About. Icograda. http://www.icograda.org/about/contact.htm. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ "The International Design Alliance Settles in Montreal.". Business Services Industry. Canadian Corporate News. May 30, 2005. http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_hb5559/is_200505/ai_n23481114. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ Kelly, Brendan (2007-05-24). "Montreal gladly reclaims its 'Hollywood North' tag". The Montreal Gazette. http://www.canada.com/cityguides/montreal/story.html?id=a5076ad1-2c87-43c1-b710-4a67a9f91617&k=39023. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ Kelly, Brendan (2008-08-13). "Montreal tries luring Hollywood back". Variety (magazine). http://www.variety.com/index.asp?layout=festivals&jump=story&id=1061&articleid=VR1117990528&cs=1. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Culture exports "should pass the test of the market"". China View. 2009-03-10. http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2009-03/10/content_10980975.htm. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ French, Michael (2007-02-09). "Ubisoft Montreal to become world's biggest studio". Develop Magazine. http://www.developmag.com/news/25657/3839m-to-help-add-1000-jobs-at-Ubisoft-Montreal. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ "The 150 richest cities in the world by GDP in 2005". RICHEST CITIES BY GDP. PricewaterhouseCoopers. March 11, 2007. http://www.citymayors.com/statistics/richest-cities-2005.html. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ "Real GDP growth (Montreal metropolitan area)" (XLS). MontrealInternational. http://www.montrealinternational.com/en/chiffres/Outlook/A_Croissance_PIB_r%C3%A9el_Montr%C3%A9al_2007-2012_ANG.xls. Retrieved on 2008-08-01.
- ^ Wingrove, Josh (June 9, 2008). "Vancouver and Montreal among 25 most livable cities". The Globe and Mail. http://www.theglobeandmail.com/servlet/story/RTGAM.20080609.wxlcities09/BNStory/lifeMain/home?cid=al_gam_mostview. Retrieved on 2008-06-19.
- ^ Twain, Mark (1881-12-10). "MARK TWAIN IN MONTREAL". New York Times (twainquotes.com). http://www.twainquotes.com/18811210.html. Retrieved on 2008-02-02.
- ^ "St. Joseph Oratory". A view on cities. 2009. http://www.aviewoncities.com/montreal/oratoirestjoseph.htm. Retrieved on 2009-03-25.
- ^ "Robinson rated ready for Dodgers in '47". The Sporting News. August 13, 1946. http://www.umass.edu/pubaffs/jackie/proballb9a.html. Retrieved on 2008-06-06.
- ^ "Ballpark financing issue may kill deal". ESPN (AP. 2004-12-15. http://sports.espn.go.com/mlb/news/story?id=1946925. Retrieved on 2009-03-23.
- ^ "Olympic Stadium – Montreal’s FIFA U-20 World Cup Venue". Canada Soccer. 2006-07-17. http://www.canadasoccer.com/eng/media/viewArtical.asp?Press_ID=2480. Retrieved on 2009-03-23.
- ^ "Rogers extends tennis sponsorship to 2008". YFile. York University. 2005-02-16. http://www.yorku.ca/yfile/archive/index.asp?Article=4039. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Quebec's Big Owe stadium debt is over". CBC.ca (Canadian Broadcasting Corporation). 2006-12-19. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/montreal/story/2006/12/19/qc-olympicstadium.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ Markham, Christina (2006-02-07). "FEATURE: It's all fun and games 'til you're up to your eyes in debt". The McGill Tribune. http://media.www.mcgilltribune.com/media/storage/paper234/news/2006/02/07/Features/Feature.Its.All.Fun.And.Games.til.Youre.Up.To.Your.Eyes.In.Debt-1601304.shtml. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ "City Council". City Hall. Ville de Montréal. http://ville.montreal.qc.ca/portal/page?_pageid=133,1297433&_dad=portal&_schema=PORTAL. Retrieved on 2008-08-02.
- ^ "The CMM at a Glance". Statistics. Montreal Metropolitan Community. http://www.cmm.qc.ca/index.php?id=334. Retrieved on 2008-08-02.
- ^ "University attendance: Montréal ranks first in relative terms and fifth in absolute terms in North America" (in English). Canada Economic Development for Quebec regions. 1996. http://www.dec-ced.gc.ca/Complements/Publications/AutresPublications-EN/tocen/css/tocen_15.htm. Retrieved on 2008-02-04.[dead link]
- ^ "McGill again tops Maclean's University Rankings", "McGill Public and Media Newsroom" November 8, 2007. Accessed May 4, 2008
- ^ "QS Top Universities: Schools" (in English). QS Quacquarelli Symonds Ltd. 2007. http://www.topuniversities.com/schools/data/school_profile/default/mcgilluniversity. Retrieved on 2008-02-04.
- ^ Turbide, Nadia (2008). "Concordia University". Histor!ca. The Canadian Encyclopedia. http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/index.cfm?PgNm=TCE&Params=U1ARTU0000783. Retrieved on 2008-06-25.
- ^ "The 350 leading higher education institutions in 2008" (PDF). Professional Ranking of World Universities. École des Mines de Paris. 2008. 33. http://www.ensmp.fr/Actualites/PR/EMP-ranking.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-11-10.
- ^ English Montreal School Board
- ^ Lester B. Pearson School Board
- ^ Commission scolaire de Montréal
- ^ Commission scolaire Marguerite-Bourgeoys
- ^ Commission scolaire Pointe-de-l'Île
- ^ "The keys to success for Smart Commuting Montreal, the Downtown Montreal Transportation Management Centre". European Platform onMobility Management. 2004. http://www.epomm.org/ecomm2004/workshops/anglais/Brun.pdf. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ "The completion of Autoroute 30". Objectives. Transports Québec. August 1, 2008. http://www.autoroute30.qc.ca/en/a30-objectifs.asp. Retrieved on 2008-08-03.
- ^ "The Bus Network: All Over Montreal" (PDF). Société de transport de Montréal. 2004. 4. http://www.stcum.qc.ca/English/en-bref/thebusnetwork.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-08-03.
- ^ Plan du métro de Montréal
- ^ Giniger, Henry (November 22, 1981). "WHAT'S DOING IN MONTREAL". New York Times. 2. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9A02EEDE1638F931A15752C1A967948260&sec=travel&spon=&pagewanted=2. Retrieved on 2008-08-03.
- ^ "Premier cuts ribbon on metro extension to Laval" (PDF). Montreal Gazette. April 26, 2007. http://www.canada.com/montrealgazette/news/story.html?id=ef3062c1-6e97-4995-95c5-f2dcad97c21c&k=89113. Retrieved on 2008-08-03.
- ^ "Montréal Public Transport System". European Metropolitan Transport Authorities. 2008-02. http://www.emta.com/article.php3?id_article=620. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ aircanada.com - About Air Canada - Corporate Profile
- ^ Air Transat
- ^ CTV.ca | Mirabel airport bids final passengers farewell
- ^ It's liftoff for AirMédic ambulance
- ^ Mirabel redécolle
- ^ Hélibellule fleet
- ^ Hélibellule fait revivre le transport des passagers à Mirabel[dead link]
- ^ a b Aéroports de Montréal Passenger Statistics
- ^ TP141 - Aircraft Movement Statistics
- ^ "Welcome to Montréal-Trudeau". Aéroports de Montréal. http://www.admtl.com/passager/services_aeriens/home.aspx. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Aer Rianta International: Worldwide Locations > Americas > Montreal" (in English). Aer Rianta International. http://www.ari.ie/?section=8&tid=1. Retrieved on 2008-02-04.
- ^ "A Brief History". General Public. Canadian Pacific Railway. http://www8.cpr.ca/cms/English/General+Public/Heritage/A+Brief+History.htm. Retrieved on 2008-08-02.[dead link]
- ^ "Where We Ship". Customers. Canadian Pacific Railway. http://www8.cpr.ca/cms/nr/cprinternet/facilitiesmap/index2.htm. Retrieved on 2008-08-02.
- ^ "Birth of Canadian National 1916-1923". Canadian National History. Canadian National Railway. http://www.cn.ca/companyinfo/history/en_AboutBirthofCanadianNational19161923.htm. Retrieved on 2008-08-02.
- ^ "Profits and Passengers - 1960-1979". Canadian National History. Canadian National Railway. http://www.cn.ca/companyinfo/history/en_AboutProfitsandpassengers19601979.htm. Retrieved on 2008-08-02.
- ^ "Sister Towns — MONTREAL". International Cooperation. Yerevan Municipality. http://yerevan.am/index.php?page=monreal&lang=eng. Retrieved on 2008-06-25.
- ^ "Window of Shanghai". Humanities and Social Sciences Library. McGill University. 2008. http://www.mcgill.ca/hssl/collections/special/shanghai/. Retrieved on 2008-06-25.
- ^ "Partner cities of Lyon and Greater Lyon" (in English). Ville de Lyon. http://www.lyon.fr/vdl/sections/en/villes_partenaires/villes_partenaires_2/?aIndex=1. Retrieved on 2008-06-25.
- ^ Mairie de Paris. "Les pactes d'amitié et de coopération". http://www.paris.fr/portail/accueil/Portal.lut?page_id=6587&document_type_id=5&document_id=16468&portlet_id=14974. Retrieved on 2007-10-14.
- ^ mastindia.com. "Little India Montreal!". http://www.mastindia.com/montreal/m_sep2k_events.html. Retrieved on 2008-02-17.
- ^ "Sister City: The City of Montreal" (in English). International Relations Division, International Peace Promotion Department. The City of Hiroshima. 2001. http://www.city.hiroshima.jp/shimin/kokusai/shimai/montreal-e.html. Retrieved on 2008-06-25.
- ^ "Manila-Montreal Sister City Agreement Holds Potential for Better Cooperation" (in English). The Republic of the Philippines. June 24, 2005. http://www.gov.ph/news/default.asp?i=10558. Retrieved on 2008-06-25.
- ^ "Busan News-Efforts increased for market exploration in N. America". Community > Notice. Busan Dong-Gu District Office. 2007-06-04. http://english.bsdonggu.go.kr/open_content/community/sub01.php?mode=view&idx=46833&page=10&searchstring=&search=. Retrieved on 2008-06-25.
[edit] Further reading
- "2006 Census of Canada". Statistics Canada. 2008. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census/index.cfm. Retrieved on 2008-05-28.
- "Montreal". 2006 Census of Canada: Community Profiles. Statistics Canada. 2008. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/profiles/community/Details/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CD&Code1=2466&Geo2=PR&Code2=24&Data=Count&SearchText=Montreal&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&Custom=. Retrieved on 2008-05-28.
- Natural Resources Canada (2005). Canadian Geographical Names: Island of Montreal. Retrieved Aug. 29, 2005.
- Michael Sletcher, 'Montréal', in James Ciment, ed., Colonial America: An Encyclopedia of Social, Political, Cultural, and Economic History, (5 vols., N.Y., 2005).
[edit] External links
![]() Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks
![]() Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote
![]() Source texts from Wikisource
Source texts from Wikisource
![]() Images and media from Commons
Images and media from Commons
![]() News stories from Wikinews
News stories from Wikinews
- Official portal of Montreal
- Official Tourism Montreal Website
- Montreal travel guide from Wikitravel
- Life in Montreal (1840–1945), Images from the McCord Museum's collections
- The Atlas of Canada: Montreal, circa 1915
- Bibliothèque Nationale du Québec[dead link] (Quebec National Library): various high-resolution maps, accessible via "Index des toponymes" / "M" / "Montréal (Québec)
- Montréal from The Canadian Encyclopedia
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||
|
|||||