Fermi problem
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In physics, particularly in physics education, a Fermi problem, Fermi question, or Fermi estimate is an estimation problem designed to teach dimensional analysis, approximation, and the importance of clearly identifying one's assumptions. Named for 20th century physicist Enrico Fermi, such problems typically involve making justified guesses about quantities that seem impossible to compute given limited available information.
Fermi was known for his ability to make good approximate calculations with little or no actual data, hence the name. One well-documented example is his estimate of the strength of the atomic bomb detonated at the Trinity test, based on the distance traveled by pieces of paper dropped from his hand during the blast.[1] Fermi's estimate of 10 kilotons of TNT was remarkably close to the now-accepted value of around 20 kilotons.
Contents |
[edit] Examples of Fermi problems
The classic Fermi problem, generally attributed to Fermi[citation needed], is "How many piano tuners are there in Chicago?" A typical solution to this problem would involve multiplying together a series of estimates that would yield the correct answer if the estimates were correct. For example, we might make the following assumptions:
- There are approximately 5,000,000 people living in Chicago.
- On average, there are two persons in each household in Chicago.
- Roughly one household in twenty has a piano that is tuned regularly.
- Pianos that are tuned regularly are tuned on average about once per year.
- It takes a piano tuner about two hours to tune a piano, including travel time.
- Each piano tuner works eight hours in a day, five days in a week, and 50 weeks in a year.
From these assumptions we can compute that the number of piano tunings in a single year in Chicago is
- (5,000,000 persons in Chicago) / (2 persons/household) × (1 piano/20 households) × (1 piano tuning per piano per year) = 125,000 piano tunings per year in Chicago.
And we can similarly calculate that the average piano tuner performs
- (50 weeks/year)×(5 days/week)×(8 hours/day)×(1 piano tuning per 2 hours per piano tuner) = 1000 piano tunings per year per piano tuner.
Dividing gives
- (125,000 piano tuning per year in Chicago) / (1000 piano tunings per year per piano tuner) = 125 piano tuners in Chicago.
A famous example of a Fermi-problem-like estimate is the Drake equation, which seeks to estimate the number of intelligent civilizations in the galaxy. The basic question of why, if there are a significant number of such civilizations, ours has never encountered any others is called the Fermi paradox.
[edit] Advantages and scope
Scientists often look for Fermi estimates of the answer to a problem before turning to more sophisticated methods to calculate a precise answer. This provides a useful check on the results: where the complexity of a precise calculation might obscure a large error, the simplicity of Fermi calculations makes them far less susceptible to such mistakes. (Performing the Fermi calculation first is preferable because the intermediate estimates might otherwise be biased by knowledge of the calculated answer.)
Fermi estimates are also useful in approaching problems where the optimal choice of calculation method depends on the expected size of the answer. For instance, a Fermi estimate might indicate whether the internal stresses of a structure are low enough that it can be accurately described by linear elasticity.
Although Fermi calculations are often not accurate, as there may be many problems with their assumptions, this sort of analysis does tell us what to look for to get a better answer. For the above example, we might try to find a better estimate of the number of pianos tuned by a piano tuner in a typical day, or look up an accurate number for the population of Chicago. It also gives us a rough estimate that may be good enough for some purposes: if we want to start a store in Chicago that sells piano tuning equipment, and we calculate that we need 10,000 potential customers to stay in business, we can reasonably assume that the above estimate is far enough below 10,000 that we should consider a different business plan (and, with a little more work, we could compute a rough upper bound on the number of piano tuners by considering the largest reasonable values that could appear in each of our assumptions).
[edit] Explanation
Fermi estimates generally work because the estimations of the individual terms are often close to correct, and over- and under-estimates help cancel each other out.
More precisely, multiplying estimates corresponds to adding their logarithms; thus one obtains a sort of Wiener process or random walk on the logarithmic scale, which diffuses as 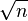 . More precisely, if one makes a Fermi estimate of n steps, with standard error σ units on the log scale, then the overall estimate will have standard error
. More precisely, if one makes a Fermi estimate of n steps, with standard error σ units on the log scale, then the overall estimate will have standard error  , since the standard deviation of a sum scales as
, since the standard deviation of a sum scales as 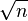 in the number of summands.
in the number of summands.
For instance, if one makes a 9-step Fermi estimate, at each step over- or under- estimating the correct number by a factor of 2, then after 9 steps the standard error will have grown by a logarithmic factor of  , so 23 = 8. Thus one will expect to be within ⅛ to 8 times the correct value – within an order of magnitude, and much less than the worst case of erring by a factor of 29 = 512. If one has a shorter chain or estimates more accurately, the overall estimate will be correspondingly better.
, so 23 = 8. Thus one will expect to be within ⅛ to 8 times the correct value – within an order of magnitude, and much less than the worst case of erring by a factor of 29 = 512. If one has a shorter chain or estimates more accurately, the overall estimate will be correspondingly better.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
[edit] External links
- The University of Maryland Physics Education Group maintains a collection of Fermi problems.
- More Fermi problems and two worked examples
- An example of a Fermi Problem relating to total gasoline consumed by cars since the invention of cars- and compares it to the output of the energy released by the sun.

